Intermixing the OPN1LW and OPN1MW Genes Disrupts the Exonic Splicing Code Causing an Array of Vision Disorders
- PMID: 34440353
- PMCID: PMC8391646
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12081180
Intermixing the OPN1LW and OPN1MW Genes Disrupts the Exonic Splicing Code Causing an Array of Vision Disorders
Abstract
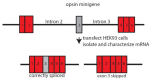
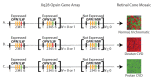
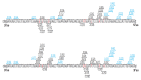
Light absorption by photopigment molecules expressed in the photoreceptors in the retina is the first step in seeing. Two types of photoreceptors in the human retina are responsible for image formation: rods, and cones. Except at very low light levels when rods are active, all vision is based on cones. Cones mediate high acuity vision and color vision. Furthermore, they are critically important in the visual feedback mechanism that regulates refractive development of the eye during childhood. The human retina contains a mosaic of three cone types, short-wavelength (S), long-wavelength (L), and middle-wavelength (M) sensitive; however, the vast majority (~94%) are L and M cones. The OPN1LW and OPN1MW genes, located on the X-chromosome at Xq28, encode the protein component of the light-sensitive photopigments expressed in the L and M cones. Diverse haplotypes of exon 3 of the OPN1LW and OPN1MW genes arose thru unequal recombination mechanisms that have intermixed the genes. A subset of the haplotypes causes exon 3- skipping during pre-messenger RNA splicing and are associated with vision disorders. Here, we review the mechanism by which splicing defects in these genes cause vision disorders.
Keywords: X-linked cone dysfunction; color vision; colorblindness; cone photopigment; exon skipping; myopia.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Neitz and J. Neitz are co-founders of SightGlass Vision and inventors of the eyeglasses currently being evaluated in NCT NCT03623074. They and the University of Washington receive licensing fees and royalties from patents related to myopia.
Figures


References
-
- Pagani F., Stuani C., Tzetis M., Kanavakis E., Efthymiadou A., Doudounakis S., Casals T., Baralle F.E. New type of disease causing mutations: The example of the composite exonic regulatory elements of splicing in CFTR exon 12. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003;12:1111–1120. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg131. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

