Structure and Function of Protein Arginine Methyltransferase PRMT7
- PMID: 34440512
- PMCID: PMC8399567
- DOI: 10.3390/life11080768
Structure and Function of Protein Arginine Methyltransferase PRMT7
Abstract
PRMT7 is a member of the protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) family, which methylates a diverse set of substrates. Arginine methylation as a posttranslational modification regulates protein-protein and protein-nucleic acid interactions, and as such, has been implicated in various biological functions. PRMT7 is a unique, evolutionarily conserved PRMT family member that catalyzes the mono-methylation of arginine. The structural features, functional aspects, and compounds that inhibit PRMT7 are discussed here. Several studies have identified physiological substrates of PRMT7 and investigated the substrate methylation outcomes which link PRMT7 activity to the stress response and RNA biology. PRMT7-driven substrate methylation further leads to the biological outcomes of gene expression regulation, cell stemness, stress response, and cancer-associated phenotypes such as cell migration. Furthermore, organismal level phenotypes of PRMT7 deficiency have uncovered roles in muscle cell physiology, B cell biology, immunity, and brain function. This rapidly growing information on PRMT7 function indicates the critical nature of context-dependent functions of PRMT7 and necessitates further investigation of the PRMT7 interaction partners and factors that control PRMT7 expression and levels. Thus, PRMT7 is an important cellular regulator of arginine methylation in health and disease.
Keywords: PRMT7; cancer; epigenetics; immunity; pluripotency; protein arginine methylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


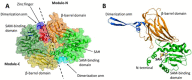
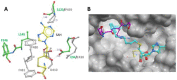
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

