Repurposing Colchicine in Treating Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34440608
- PMCID: PMC8398430
- DOI: 10.3390/life11080864
Repurposing Colchicine in Treating Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) had caused huge health losses worldwide. Several drugs had been applied to treat patients with COVID-19, and repurposing colchicine had been proposed for its anti-inflammatory properties via several pathways. In this systematic review, we evaluated the effects of colchicine treatment. From inception to May 31, 2021, databases, including PubMed, EMbase, medRxiv, and Research Square were searched, and 11 studies were enrolled. A total of 17,205 COVID-19 patients with male predominance (62.9%) were analyzed. Patients with colchicine treatment had a significantly lower risk of mortality (odds ratio (OR): 0.57, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.38-0.87, I2: 72%; p < 0.01) and a non-significantly lower rate of mechanical ventilation (OR: 0.67, 95%CI: 0.39-1.15). The side effects were mild and not significantly different (OR: 2.03, 95%CI: 0.51-8.09). Subgroup analysis with randomized controlled trials showed no statistically significant difference in the mortality (OR: 0.80, 95%CI: 0.44-1.46, I2: 33%; p = 0.22). In conclusion, our meta-analysis found that colchicine treatment was associated with a significantly lower risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19. However, this benefit was not observed in the subgroup analysis of randomized controlled trials. Further randomized controlled studies are required to confirm the potential benefits of colchicine treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; colchicine; immunomodulation; novel coronavirus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
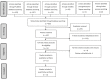
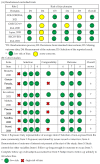




References
-
- Our World in Data Mortality Risk of COVID-19. [(accessed on 1 June 2021)]; Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/mortality-risk-COVID.
-
- Johns Hopkins University & Medicine Mortality Analyses. [(accessed on 1 June 2021)]; Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/data/mortality.
-
- Chen C.C., Tseng C.Y., Choi W.M., Lee Y.C., Su T.H., Hsieh C.Y., Chang C.M., Weng S.L., Liu P.H., Tai Y.L., et al. Taiwan government-guided strategies contributed to combating and controlling COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Public Health. 2020;8:547423. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.547423. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

