Tuning Monocytes and Macrophages for Personalized Therapy and Diagnostic Challenge in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 34440629
- PMCID: PMC8392289
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10081860
Tuning Monocytes and Macrophages for Personalized Therapy and Diagnostic Challenge in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
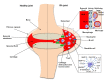
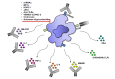
Monocytes/macrophages play a central role in chronic inflammatory disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Activation of these cells results in the production of various mediators responsible for inflammation and RA pathogenesis. On the other hand, the depletion of macrophages using specific antibodies or chemical agents can prevent their synovial tissue infiltration and subsequently attenuates inflammation. Their plasticity is a major feature that helps the switch from a pro-inflammatory phenotype (M1) to an anti-inflammatory state (M2). Therefore, understanding the precise strategy targeting pro-inflammatory monocytes/macrophages should be a powerful way of inhibiting chronic inflammation and bone erosion. In this review, we demonstrate potential consequences of different epigenetic regulations on inflammatory cytokines production by monocytes. In addition, we present unique profiles of monocytes/macrophages contributing to identification of new biomarkers of disease activity or predicting treatment response in RA. We also outline novel approaches of tuning monocytes/macrophages by biologic drugs, small molecules or by other therapeutic modalities to reduce arthritis. Finally, the importance of cellular heterogeneity of monocytes/macrophages is highlighted by single-cell technologies, which leads to the design of cell-specific therapeutic protocols for personalized medicine in RA in the future.
Keywords: biologics; biomarkers; epigenetics; heterogeneity; macrophages; monocytes; personalized therapy; rheumatoid arthritis; single-cell sequencing; small molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Horizon 2020 Framework Programme EULAR’s Position and Recommendations. [(accessed on 11 November 2011)]; Available online: https://www.eular.org/myUploadData/files/EU_Horizon_2020_EULAR_position_....
-
- Haringman J.J., Gerlag D.M., Zwinderman A.H., Smeets T.J., Kraan M.C., Baeten D., McInnes I.B., Bresnihan B., Tak P.P. Synovial tissue macrophages: A sensitive biomarker for response to treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005;64:834–838. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.029751. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

