Liquid Biopsy for Disease Monitoring in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The Link between Biology and the Clinic
- PMID: 34440680
- PMCID: PMC8394732
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10081912
Liquid Biopsy for Disease Monitoring in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The Link between Biology and the Clinic
Abstract
Introduction: Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) analysis offers a non-invasive method to identify sensitising and resistance mutations in advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) patients. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) of circulating free DNA (cfDNA) is a valuable tool for mutations detection and disease's clonal monitoring.
Material and methods: An amplicon-based targeted gene NGS panel was used to analyse 101 plasma samples of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with known oncogenic mutations, mostly EGFR mutations, serially collected at different clinically relevant time points of the disease.
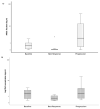
Results: The variant allelic frequency (VAF) monitoring in consecutive plasma samples demonstrated different molecular response and progression patterns. The decrease in or the clearance of the mutant alleles was associated with response and the increase in or the emergence of novel alterations with progression. At the best response, the median VAF was 0% (0.0% to 3.62%), lower than that at baseline, with a median of 0.53% (0.0% to 9.9%) (p = 0.004). At progression, the VAF was significantly higher (median 4.67; range: 0.0-36.9%) than that observed at the best response (p = 0.001) and baseline (p = 0.006). These variations anticipated radiographic changes in most cases, with a median time of 0.86 months. Overall, the VAF evolution of different oncogenic mutations predicts clinical outcomes.
Conclusion: The targeted NGS of circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) has clinical utility to monitor treatment response in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: adenocarcinoma; cell-free DNA; clinical outcomes; liquid biopsy; lung cancer; next-generation sequencing; tumour-free DNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Kris M.G., Johnson B.E., Berry L.D., Kwiatkowski D.J., Iafrate A.J., Wistuba I.I., Varella-Garcia M., Franklin W.A., Aronson S.L., Su P.-F., et al. Using multiplexed assays of oncogenic drivers in lung cancers to select targeted drugs. JAMA. 2014;311:1998–2006. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.3741. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Planchard D., Popat S., Kerr K., Novello S., Smit E.F., Faivre-Finn C., Mok T.S., Reck M., Van Schil P.E., Hellmann M.D., et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018;29:iv192–iv237. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy275. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jahr S., Hentze H., Englisch S., Hardt D., Fackelmayer F.O., Hesch R.D., Knippers R. DNA fragments in the blood plasma of cancer patients: Quantitations and evidence for their origin from apoptotic and necrotic cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1659–1665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

