The Roadmap of RANKL/RANK Pathway in Cancer
- PMID: 34440747
- PMCID: PMC8393235
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10081978
The Roadmap of RANKL/RANK Pathway in Cancer
Abstract
The receptor activator of the nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)/RANK signaling pathway was identified in the late 1990s and is the key mediator of bone remodeling. Targeting RANKL with the antibody denosumab is part of the standard of care for bone loss diseases, including bone metastases (BM). Over the last decade, evidence has implicated RANKL/RANK pathway in hormone and HER2-driven breast carcinogenesis and in the acquisition of molecular and phenotypic traits associated with breast cancer (BCa) aggressiveness and poor prognosis. This marked a new era in the research of the therapeutic use of RANKL inhibition in BCa. RANKL/RANK pathway is also an important immune mediator, with anti-RANKL therapy recently linked to improved response to immunotherapy in melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and renal cell carcinoma (RCC). This review summarizes and discusses the pre-clinical and clinical evidence of the relevance of the RANKL/RANK pathway in cancer biology and therapeutics, focusing on bone metastatic disease, BCa onset and progression, and immune modulation.
Keywords: RANK ligand (RANKL); bone metastasis; bone-targeted agent; breast cancer; drug repurposing; receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB (RANK); targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
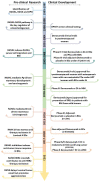

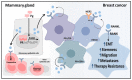
References
-
- Yasuda H., Shima N., Nakagawa N., Yamaguchi K., Kinosaki M., Mochizuki S., Tomoyasu A., Yano K., Goto M., Murakami A., et al. Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1998;95:3597–3602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.7.3597. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schramek D., Leibbrandt A., Sigl V., Kenner L., Pospisilik J.A., Lee H.J., Hanada R., Joshi P.A., Aliprantis A., Glimcher L., et al. Osteoclast differentiation factor RANKL controls development of progestin-driven mammary cancer. Nature. 2010;468:98–102. doi: 10.1038/nature09387. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

