Development of an Imaging Technique for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy
- PMID: 34440904
- PMCID: PMC8392566
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10082135
Development of an Imaging Technique for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy
Abstract
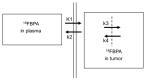
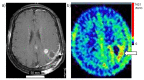
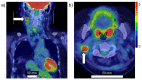
The development of 4-10B-borono-2-18F-fluoro-L-phenylalanine (18FBPA) for use in positron emission tomography (PET) has contributed to the progress of boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). 18FBPA has shown similar pharmacokinetics and distribution to 4-10B-borono-L-phenylalanine (BPA) under various conditions in many animal studies. 18FBPA PET is useful for treatment indication. A higher 18FBPA accumulation ratio of the tumor to the surrounding normal tissue (T/N ratio) indicates that a superior treatment effect is expected. In clinical settings, a T/N ratio of higher than 2.5 or 3 is often used for patient selection. Moreover, 18FBPA PET is useful for predicting the 10B concentration delivered to the tumor and surrounding normal tissues, enabling high-precision treatment planning. Precise dose prediction using 18FBPA PET data has greatly improved the treatment accuracy of BNCT. However, the methodology used for the data analysis of 18FBPA PET findings varies; thus, data should be evaluated using a consistent methodology so as to be more reliable. In addition to PET applications, the development of 18FBPA as a contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging that combines gadolinium and 10B is also in progress.
Keywords: 18FBPA; BNCT; PET.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
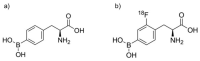

Similar articles
-
4-Borono-2-18F-fluoro-L-phenylalanine PET for boron neutron capture therapy-oriented diagnosis: overview of a quarter century of research.Ann Nucl Med. 2019 Apr;33(4):223-236. doi: 10.1007/s12149-019-01347-8. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Ann Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30820862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-invasive estimation of 10 B-4-borono-L-phenylalanine-derived boron concentration in tumors by PET using 4-borono-2-18 F-fluoro-phenylalanine.Cancer Sci. 2018 May;109(5):1617-1626. doi: 10.1111/cas.13553. Epub 2018 Apr 15. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29498142 Free PMC article.
-
Similar T/N ratio between 18F-FBPA diagnostic and BPA therapeutic dosages for boron neutron capture therapy in orthotropic tongue cancer model.Ann Nucl Med. 2020 Jan;34(1):58-64. doi: 10.1007/s12149-019-01415-z. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Ann Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 31650410
-
PET pharmacokinetic analysis to estimate boron concentration in tumor and brain as a guide to plan BNCT for malignant cerebral glioma.Appl Radiat Isot. 2009 Jul;67(7-8 Suppl):S348-50. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2009.03.061. Epub 2009 Mar 27. Appl Radiat Isot. 2009. PMID: 19375930
-
Recent Development of Radiofluorination of Boron Agents for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy of Tumor: Creation of 18F-Labeled C-F and B-F Linkages.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jan 9;16(1):93. doi: 10.3390/ph16010093. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678590 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Viability of Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for Personalized Radiation Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 10;14(12):2865. doi: 10.3390/cancers14122865. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Boron in My Mind: A Comprehensive Review of the Evolution of the Diverse Syntheses of 4-Borono-l-Phenylalanine, the Leading Agent for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy.ChemMedChem. 2025 Jun 2;20(11):e202500059. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202500059. Epub 2025 Apr 14. ChemMedChem. 2025. PMID: 40074685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in 64Cu/67Cu-Based Radiopharmaceuticals.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 23;24(11):9154. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119154. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation between L-amino acid transporter 1 expression and 4-borono-2-18 F-fluoro-phenylalanine accumulation in humans.Cancer Med. 2023 Nov;12(21):20564-20572. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6635. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37881128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ishiwata K., Ido T., Mejia A.A., Ichihashi M., Mishima Y. Synthesis and radiation dosimetry of 4-borono-2-[18F]fluoro-d,l-phenylalanine: A target compound for PET and boron neutron capture therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1991;42:325–328. doi: 10.1016/0883-2889(91)90133-L. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Imahori Y., Ueda S., Ohmori Y., Kusuki T., Ono K., Fujii R., Ido T. Fluorine-18-labeled fluoroboronophenylalanine PET in patients with glioma. J. Nucl. Med. 1998;39:325–333. - PubMed
-
- Hanaoka K., Watabe T., Naka S., Kanai Y., Ikeda H., Horitsugi G., Kato H., Isohashi K., Shimosegawa E., Hatazawa J. FBPA PET in boron neutron capture therapy for cancer: Prediction of (10)B concentration in the tumor and normal tissue in a rat xenograft model. EJNMMI Res. 2014;4:1–8. doi: 10.1186/s13550-014-0070-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

