Mechanisms of Smoothened Regulation in Hedgehog Signaling
- PMID: 34440907
- PMCID: PMC8391454
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10082138
Mechanisms of Smoothened Regulation in Hedgehog Signaling
Abstract
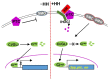
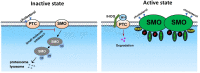
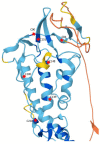
The seven-transmembrane protein, Smoothened (SMO), has shown to be critical for the hedgehog (HH) signal transduction on the cell membrane (and the cilium in vertebrates). SMO is subjected to multiple types of post-translational regulations, including phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and sumoylation, which alter SMO intracellular trafficking and cell surface accumulation. Recently, SMO is also shown to be regulated by small molecules, such as oxysterol, cholesterol, and phospholipid. The activity of SMO must be very well balanced by these different mechanisms in vivo because the malfunction of SMO will not only cause developmental defects in early stages, but also induce cancers in late stages. Here, we discuss the activation and inactivation of SMO by different mechanisms to better understand how SMO is regulated by the graded HH signaling activity that eventually governs distinct development outcomes.
Keywords: cholesterol; hedgehog signaling; phospholipid; phosphorylation; smoothened; ubiquitination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

