Analytical Rheology of Honey: A State-of-the-Art Review
- PMID: 34441487
- PMCID: PMC8391245
- DOI: 10.3390/foods10081709
Analytical Rheology of Honey: A State-of-the-Art Review
Abstract
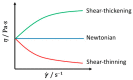
Honey has been used as a nutraceutical product since ancient times due to its nutritional and medicinal properties. Honey rheology influences its organoleptic properties and is relevant for processing and quality control. This review summarizes the rheological behaviour of honeys of different botanical source(s) and geographical locations that has been described in the literature, focusing on the relation between rheological parameters, honey composition (moisture, water activity, sugar content, presence of colloidal matter) and experimental conditions (temperature, time, stress, shear rate). Both liquid and crystallized honeys have been addressed. Firstly, the main mathematical models used to describe honey rheological behaviour are presented highlighting moisture and temperature effects. Then, rheological data from the literature regarding distinct honey types from different countries is analysed and results are compared. Although most honeys are Newtonian fluids, interesting shear-thinning and thixotropic as well as anti-thixotropic behaviour have been described for some types of honey. Rheological parameters have also been successfully applied to identify honey adulteration and to discriminate between different honey types. Several chemometric techniques have also been employed to obtain the complex relationships between honey physicochemical and rheological properties, including partial least squares (PLS), principal component analysis (PCA) and artificial neural networks (ANN).
Keywords: adulteration; honey; moisture; rheology; temperature; viscosity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Codex Alimentarius . International Standard for Honey CXS 12-1981. Amended in 2019; FAO; Rome, Italy: 1981. pp. 1–8. Adopted in 1981.
-
- Gómez-Díaz D., Navaza J.M., Quintáns-Riveiro L.C. Rheological behaviour of Galician honeys. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2006;222:439–442. doi: 10.1007/s00217-005-0120-0. - DOI
-
- Faustino C., Pinheiro L. Antimicrobial properties and therapeutic benefits of honey in the quest for more efficient antimicrobial agents. In: Méndez-Vilas A., editor. The Battle Against Microbial Pathogens: Basic Science, Technological Advances and Educational Programs. Volume 1. Formatex; Badajoz, Spain: 2015. pp. 98–108.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources