Rapid Antigen Test Combined with Chest Computed Tomography to Rule Out COVID-19 in Patients Admitted to the Emergency Department
- PMID: 34441750
- PMCID: PMC8397078
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10163455
Rapid Antigen Test Combined with Chest Computed Tomography to Rule Out COVID-19 in Patients Admitted to the Emergency Department
Abstract
Objective: Correct and timely identification of SARS-CoV-2-positive patients is critical in the emergency department (ED) prior to admission to medical wards. Antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic tests (Ag-RDTs) are a rapid alternative to Reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for the diagnosis of COVID-19 but have lower sensitivity.
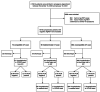
Methods: We evaluated the performance in real-life conditions of a strategy combining Ag-RDT and chest computed tomography (CT) to rule out COVID-19 infection in 1015 patients presenting in the ED between 16 November 2020 and 18 January 2021 in order to allow non-COVID-19 patients to be hospitalized in dedicated units directly. The combined strategy performed in the ED for patients with COVID-19 symptoms was assessed and compared with RT-PCR.
Results: Compared with RT-PCR, the negative predictive value was 96.7% for Ag-RDT alone, 98.5% for Ag-RDT/CT combined, and increased to 100% for patients with low viral load.
Conclusion: A strategy combining Ag-RDT and chest CT is effective in ruling out COVID-19 in ED patients with high precision.
Keywords: RT-PCR; SARS-CoV2; antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic test; chest computed tomography; emergency department.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Thibon E., Bobbia X., Blanchard B., Masia T., Palmier L., Tendron L., de la Coussaye J.E., Claret P.G. Association between Mortality and Waiting Time in Emergency Room among Adults Hospitalized for Medical Etiologies. Ann. Fr. Méd. Urgence. 2019;9:229–234. doi: 10.3166/afmu-2019-0151. - DOI
-
- Chen J.Y., Chang F.Y., Lin C.S., Wang C.H., Tsai S.H., Lee C.C., Chen S.J. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Loading and Quality of an Emergency Department in Taiwan: Enlightenment from a Low-Risk Country in a Public Health Crisis. J. Clin. Med. 2021;10:1150. doi: 10.3390/jcm10061150. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pilarowski G., Marquez C., Rubio L., Peng J., Martinez J., Black D., Chamie G., Jones D., Jacobo J., Tulier-Laiwa V., et al. Field performance and public health response using the BinaxNOW TM Rapid SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection assay during community-based testing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020:ciaa1890. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1890. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

