Urine Phenylacetylglutamine Determination in Patients with Hyperphenylalaninemia
- PMID: 34441968
- PMCID: PMC8396897
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10163674
Urine Phenylacetylglutamine Determination in Patients with Hyperphenylalaninemia
Abstract
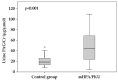
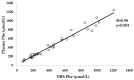
Phenylketonuria (PKU), an autosomal-recessive inborn error of phenylalanine (Phe) metabolism is the most prevalent disorder of amino acid metabolism. Currently, clinical follow-up relies on frequent monitoring of Phe levels in blood. We hypothesize that the urine level of phenylacetylglutamine (PAG), a phenyl-group marker, could be used as a non-invasive biomarker. In this cross-sectional study, a validated liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS) method was used for urinary PAG quantification in 35 participants with hyperphenylalaninemia (HPA) and 33 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. We have found that (a) PKU patients present higher urine PAG levels than healthy control subjects, and that (b) there is a significant correlation between urine PAG and circulating Phe levels in patients with HPA. In addition, we show a significant strong correlation between Phe levels from venous blood samples and from capillary finger-prick dried blood spot (DBS) samples collected at the same time in patients with HPA. Further research in order to assess the potential role of urine PAG as a non-invasive biomarker in PKU is warranted.
Keywords: biomarkers; dried blood spot; phenylacetylglutamine; phenylalanine; phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency; phenylketonuria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Van Wegberg A.M.J., MacDonald A., Ahring K., Bélanger-Quintana A., Blau N., Bosch A.M., Burlina A., Campistol J., Feillet F., Giżewska M., et al. The complete European guidelines on phenylketonuria: Diagnosis and treatment. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017;12:162. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0685-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Singh R.H., Cunningham A.C., Mofidi S., Douglas T.D., Frazier D.M., Hook D.G., Jeffers L., McCune H., Moseley K.D., Ogata B., et al. Updated, web-based nutrition management guideline for PKU: An evidence and consensus based approach. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2016;118:72–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2016.04.008. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

