Lignocellulosic Biomass-Derived Carbon Electrodes for Flexible Supercapacitors: An Overview
- PMID: 34443094
- PMCID: PMC8401572
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14164571
Lignocellulosic Biomass-Derived Carbon Electrodes for Flexible Supercapacitors: An Overview
Abstract
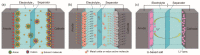
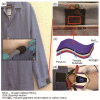
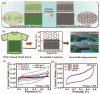
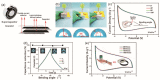
With the increasing demand for high-performance electronic devices in smart textiles, various types of flexible/wearable electronic device (i.e., supercapacitors, batteries, fuel cells, etc.) have emerged regularly. As one of the most promising wearable devices, flexible supercapacitors from a variety of electrode materials have been developed. In particular, carbon materials from lignocellulosic biomass precursor have the characteristics of low cost, natural abundance, high specific surface area, excellent electrochemical stability, etc. Moreover, their chemical structures usually contain a large number of heteroatomic groups, which greatly contribute to the capacitive performance of the corresponding flexible supercapacitors. This review summarizes the working mechanism, configuration of flexible electrodes, conversion of lignocellulosic biomass-derived carbon electrodes, and their corresponding electrochemical properties in flexible/wearable supercapacitors. Technology challenges and future research trends will also be provided.
Keywords: electrochemical performance; electrode; flexible/wearable supercapacitor; lignocellulose-derived carbon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Yu Z., Tetard L., Zhai L., Thomas J. Supercapacitor electrode materials: Nanostructures from 0 to 3 dimensions. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015;8:702–730. doi: 10.1039/C4EE03229B. - DOI
-
- Faraji S., Ani F.N. The development supercapacitor from activated carbon by electroless plating—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015;42:823–834. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.10.068. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

