Orexins/Hypocretins and Cancer: A Neuropeptide as Emerging Target
- PMID: 34443437
- PMCID: PMC8398691
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26164849
Orexins/Hypocretins and Cancer: A Neuropeptide as Emerging Target
Abstract
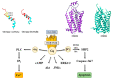
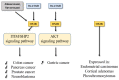
Over 20 years ago, orexin neuropeptides (Orexin-A/hypocretin-1 and Orexin-B/hypocretins-2) produced from the same precursor in hypothalamus were identified. These two neurotransmitters and their receptors (OX1R and OX1R), present in the central and peripheral nervous system, play a major role in wakefulness but also in drug addiction, food consumption, homeostasis, hormone secretion, reproductive function, lipolysis and blood pressure regulation. With respect to these biological functions, orexins were involved in various pathologies encompassing narcolepsy, neurodegenerative diseases, chronic inflammations, metabolic syndrome and cancers. The expression of OX1R in various cancers including colon, pancreas and prostate cancers associated with its ability to induce a proapoptotic activity in tumor cells, suggested that the orexins/OX1R system could have a promising therapeutic role. The present review summarizes the relationship between cancers and orexins/OX1R system as an emerging target.
Keywords: GPCR; apoptosis; cancer; gastroenterology; neuropeptide; orexins.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors don’t have any conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- de Lecea L., Kilduff T.S., Peyron C., Gao X., Foye P.E., Danielson P.E., Fukuhara C., Battenberg E.L., Gautvik V.T., Bartlett F.S., II, et al. The hypocretins: Hypothalamus-specific peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1998;95:322–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.1.322. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sakurai T., Amemiya A., Ishii M., Matsuzaki I., Chemelli R.M., Tanaka H., Williams S.C., Richardson J.A., Kozlowski G.P., Wilson S., et al. Orexins and orexin receptors: A family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell. 1998;92:573–585. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80949-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

