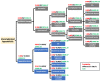
Cost-Utility Analysis of Antibiotic Therapy versus Appendicectomy for Acute Uncomplicated Appendicitis
- PMID: 34444222
- PMCID: PMC8392297
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18168473
Cost-Utility Analysis of Antibiotic Therapy versus Appendicectomy for Acute Uncomplicated Appendicitis
Abstract
Background: Current UK National Health Service (NHS) guidelines recommend appendicectomy as gold standard treatment for acute uncomplicated appendicitis. However, an alternative non-surgical management involves administrating antibiotic-only therapy with significantly lower costs. Therefore, a UK-based cost-utility analysis (CUA) was performed to compare appendicectomy with an antibiotic-only treatment from an NHS perspective.
Methods: This economic evaluation modelled health-outcome data using the ACTUAA (2021) prospective multicentre trial. The non-randomised control trial followed 318 patients given either antibiotic therapy or appendicectomy, with quality of life (QOL) assessed using the SF-12 questionnaires administered 1-year post-treatment. A CUA was conducted over a 1-year time horizon, measuring benefits in quality adjusted life years (QALYs) and costs in pound sterling using a propensity score-matched approach to control for selection based on observable factors.
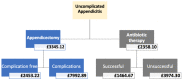
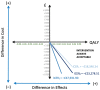
Results: The CUA produced an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of -GBP 23,278.51 (-EUR 27,227.80) per QALY. Therefore, for each QALY gained using antibiotic-only treatment instead of appendicectomy, an extra GBP 23,278.51 was saved. Additionally, two sensitivity analyses were conducted to account for post-operative or post-treatment complications. The antibiotic-only option remained dominant in both scenarios.
Conclusion: While the results do not rely on a randomized sample, the analysis based on a 1-year follow-up suggested that antibiotics were largely more cost-effective than appendicectomy and led to improved QOL outcomes for patients. The ICER value of -GBP 23,278.51 demonstrates that the NHS must give further consideration to the current gold standard treatment in acute uncomplicated appendicitis.
Keywords: acute uncomplicated appendicitis; antibiotic therapy; appendicectomy; cost-utility; economic evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- NICE Appendicitis. [(accessed on 12 February 2021)];2020 Available online: https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/appendicitis/
-
- NHS Appendicitis. [(accessed on 12 February 2021)];2019 Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/appendicitis/
-
- NICE Scenario: Managing Suspected Appendicitis. [(accessed on 9 February 2021)];2020 Available online: https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/appendicitis/management/managing-suspecte...
-
- Di Saverio S., Podda M., De Simone B., Ceresoli M., Augustin G., Gori A., Boermeester M., Sartelli M., Coccolini F., Tarasconi A., et al. Diagnosis and treatment of acute appendicitis: 2020 update of the WSES Jesusalem guidelines. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2020;15:1–42. doi: 10.1186/s13017-020-00306-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials