Dying "from" or "with" COVID-19 during the Pandemic: Medico-Legal Issues According to a Population Perspective
- PMID: 34444600
- PMCID: PMC8393539
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18168851
Dying "from" or "with" COVID-19 during the Pandemic: Medico-Legal Issues According to a Population Perspective
Abstract
There is still a lack of knowledge concerning the pathophysiology of death among COVID-19-deceased patients, and the question of whether a patient has died with or due to COVID-19 is still very much debated. In Italy, all deaths of patients who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 are defined as COVID-19-related, without considering pre-existing diseases that may either contribute to or even cause death. Our study included nine subjects from two different nursing homes (Cases 1-4, Group A; Cases 5-9, Group B). The latter included patients who presumably died from CO poisoning due to a heating system malfunction. All subjects tested positive for COVID-19 both ante- and post-mortem and were examined using post-mortem computed tomography prior to autopsy. COVID-19 was determined to be a contributing cause in the deaths of four out of nine subjects (death due to COVID-19; i.e., pneumonia and sudden cardiac death). In the other five cases, for which CO poisoning was identified as the cause of death, the infection presumably had no role in exitus (death with COVID-19). In our attempt to classify our patients as dying with or due to COVID-19, we found the use of complete assessments (both histological analyses and computed tomography examination) fundamental.
Keywords: CO intoxication; COVID-19; causality; pneumonia; post-mortem computed tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
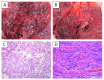
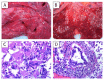

References
-
- World Health Organization. [(accessed on 31 March 2021)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/
-
- Sharma R., Agarwal M., Gupta M., Somendra S., Saxena S.K. Clinical Characteristics and Differential Clinical Diagnosis of Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) In: Saxena S., editor. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Medical Virology: From Pathogenesis to Disease Control. Springer; Singapore: 2020. pp. 55–70.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

