Anticancer Activity of Propolis and Its Compounds
- PMID: 34444754
- PMCID: PMC8399583
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13082594
Anticancer Activity of Propolis and Its Compounds
Abstract
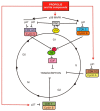
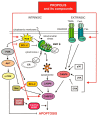
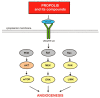
Propolis is a natural material that honey bees (Apis mellifera) produce from various botanical sources. The therapeutic activity of propolis, including antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory effects, have been known since antiquity. Cancer is one of the major burdens of disease worldwide, therefore, numerous studies are being conducted to develop new chemotherapeutic agents and treatments for cancer. Propolis is a rich source of biologically active compounds, which affect numerous signaling pathways regulating crucial cellular processes. The results of the latest research show that propolis can inhibit proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis of cancer cells and stimulate apoptosis. Moreover, it may influence the tumor microenvironment and multidrug resistance of cancers. This review briefly summarizes the molecular mechanisms of anticancer activity of propolis and its compounds and highlights the potential benefits of propolis to reduce the side effects of chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Keywords: angiogenesis; apoptosis; autophagy; cancer; cancer therapy; cell proliferation; cytotoxicity; metastasis; propolis; propolis compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zabaiou N., Fouache A., Trousson A., Buñay-Noboa J., Marceau G., Sapin V., Zellagui A., Baron S., Lahouel M., Lobaccaro J.M.A. Ethanolic extract of Algerian propolis decreases androgen receptor transcriptional activity in cultured LNCaP cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019;189:108–115. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.02.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Santos L.M., Fonseca M.S., Sokolonski A.R., Deegan K.R., Araújo R.P.C., Umsza-Guez M.A., Barbosa J.D.V., Portela R.D., Machado B.A.S. Propolis: Types, composition, biological activities, and veterinary product patent prospecting. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020;100:1369–1382. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stojanović S., Najman S.J., Bogdanova-Popov B., Najman S.S. Propolis: Chemical composition, biological and pharmacological activity—A Review. Acta Med. Median. 2020;59:108–113. doi: 10.5633/amm.2020.0215. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

