The Emerging Role of Nutraceuticals in Cardiovascular Calcification: Evidence from Preclinical and Clinical Studies
- PMID: 34444763
- PMCID: PMC8401694
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13082603
The Emerging Role of Nutraceuticals in Cardiovascular Calcification: Evidence from Preclinical and Clinical Studies
Abstract
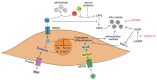
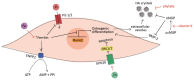
Cardiovascular calcification is the ectopic deposition of calcium-phosphate crystals within the arterial wall and the aortic valve leaflets. This pathological process leads to increased vascular stiffness, reduced arterial elasticity, and aortic valve stenosis, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Although cardiovascular calcification is an increasing health care burden, to date no medical therapies have been approved for treating or preventing it. Considering the current lack of therapeutic strategies and the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular calcification, the investigation of some nutraceuticals to prevent this pathological condition has become prevalent in recent years. Recent preclinical and clinical studies evaluated the potential anti-calcific role of nutraceuticals (including magnesium, zinc, iron, vitamin K, and phytate) in the progression of vascular calcification, providing evidence for their dietary supplementation, especially in high-risk populations. The present review summarizes the current knowledge and latest advances for nutraceuticals with the most relevant preclinical and clinical data, including magnesium, zinc, iron, vitamin K, and phytate. Their supplementation might be recommended as a cost-effective strategy to avoid nutritional deficiency and to prevent or treat cardiovascular calcification. However, the optimal dose of nutraceuticals has not been identified and large interventional trials are warranted to support their protective effects on cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: nutraceuticals; nutrition; vascular calcification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Schantl A.E., Ivarsson M.E., Leroux J.-C. Investigational Pharmacological Treatments for Vascular Calcification. Adv. Ther. 2019;2:1800094. doi: 10.1002/adtp.201800094. - DOI
-
- Bikbov B., Purcell C.A., Levey A.S., Smith M., Abdoli A., Abebe M., Adebayo O.M., Afarideh M., Agarwal S.K., Agudelo-Botero M., et al. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2020;395:709–733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30045-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Osnabrugge R.L.J., Mylotte D., Head S.J., van Mieghem N.M., Nkomo V.T., Lereun C.M., Bogers A.J.J.C., Piazza N., Kappetein A.P. Aortic stenosis in the elderly: Disease prevalence and number of candidates for transcatheter aortic valve replacement: A meta-analysis and modeling study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013;62:1002–1012. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

