Gibberellin Signaling Promotes the Secondary Growth of Storage Roots in Panax ginseng
- PMID: 34445398
- PMCID: PMC8395461
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22168694
Gibberellin Signaling Promotes the Secondary Growth of Storage Roots in Panax ginseng
Abstract
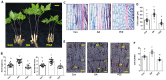
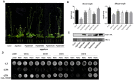
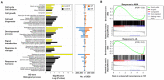
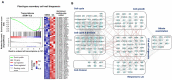
Gibberellins (GAs) are an important group of phytohormones associated with diverse growth and developmental processes, including cell elongation, seed germination, and secondary growth. Recent genomic and genetic analyses have advanced our knowledge of GA signaling pathways and related genes in model plant species. However, functional genomics analyses of GA signaling pathways in Panax ginseng, a perennial herb, have rarely been carried out, despite its well-known economical and medicinal importance. Here, we conducted functional characterization of GA receptors and investigated their physiological roles in the secondary growth of P. ginseng storage roots. We found that the physiological and genetic functions of P. ginseng gibberellin-insensitive dwarf1s (PgGID1s) have been evolutionarily conserved. Additionally, the essential domains and residues in the primary protein structure for interaction with active GAs and DELLA proteins are well-conserved. Overexpression of PgGID1s in Arabidopsis completely restored the GA deficient phenotype of the Arabidopsis gid1a gid1c (atgid1a/c) double mutant. Exogenous GA treatment greatly enhanced the secondary growth of tap roots; however, paclobutrazol (PCZ), a GA biosynthetic inhibitor, reduced root growth in P. ginseng. Transcriptome profiling of P. ginseng roots revealed that GA-induced root secondary growth is closely associated with cell wall biogenesis, the cell cycle, the jasmonic acid (JA) response, and nitrate assimilation, suggesting that a transcriptional network regulate root secondary growth in P. ginseng. These results provide novel insights into the mechanism controlling secondary root growth in P. ginseng.
Keywords: GID1s; Panax ginseng; cell wall biogenesis; gibberellins; phytohormones; storage root secondary growth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hu S.Y. The genusPanax (ginseng) in Chinese medicine. Econ. Bot. 1976;30:11–28. doi: 10.1007/BF02866780. - DOI
-
- Luo H., Sun C., Sun Y.Z., Wu Q., Li Y., Song J.Y., Niu Y.Y., Cheng X.L., Liu J.Y., Steinmetz A., et al. Analysis of the transcriptome of Panax notoginseng root uncovers putative triterpene saponin-biosynthetic genes and genetic markers. BMC Genom. 2011;12:S5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-S5-S5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choi H.I.E., Waminal N., Park H.M., Kim N.-C., Choi B.S., Park M., Choi D., Lim Y.P., Kwon S.-J., Park B.-S., et al. Major repeat components covering one-third of the ginseng (P anax ginseng CA Meyer) genome and evidence for allotetraploidy. Plant. J. 2014;77:906–916. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12441. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

