Prevalence of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in a Chinese multidrug-resistant TB cohort after redefinition
- PMID: 34446095
- PMCID: PMC8393791
- DOI: 10.1186/s13756-021-00995-8
Prevalence of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in a Chinese multidrug-resistant TB cohort after redefinition
Abstract
Objectives: Recently, the definition of extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB) has been revised. In this study, we conducted a descriptive and retrospective study to determine the prevalence of XDR-TB in a Chinese multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) cohort.
Methods: Broth microdilution method was performed to determine in vitro susceptibilities of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) isolates to (FQs), bedaquiline (BDQ) and linezolid (LZD). The putative drug target genes conferring drug resistance were screened by DNA sequencing.
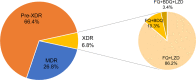
Results: A total of 425 MDR-TB isolates were included from 13 pilots in China. LZD and BDQ resistance were noted in 30 (7.1%) and 10 (2.4%) isolates. On the basis of latest definitions, 114 (26.8%) were MDR-TB, 282 (66.4%) were pre-XDR-TB, and 29 (6.8%) were XDR-TB. Among 311 FQ-resistant isolates, 265 harbored genetic mutations within QRDRs. The most common mutations were observed at codon 94 of gyrA, accounting for 47.2% of FQ-resistant MTB isolates. Only mutations within the Rv0678 gene were found to confer BDQ resistance in our cohort, conferring 40.0% of BDQ resistance. For LZD resistance, 53.3% of LZD-resistant isolates carried genetic mutations in rplC or 23S rRNA. The most frequent mutation was Cys154Arg in the rplC gene. In addition, we recorded two MDR-TB patients with resistance to both BDQ and LZD, of which one patient experienced continuous positive culture of MTB despite inclusion of efficacious moxifloxacin.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that the low prevalence of XDR-TB holds great promise for MDR-TB treatment with WHO-endorsed regimens containing BDQ-LZD combination, whereas the high prevalence of FQ-resistance in MDR-TB patients warrants national attention.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Susceptibility; XDR.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors: no conflicts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In Vitro Drug Susceptibility of Bedaquiline, Delamanid, Linezolid, Clofazimine, Moxifloxacin, and Gatifloxacin against Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Beijing, China.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Sep 22;61(10):e00900-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00900-17. Print 2017 Oct. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28739779 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging threat of fluroquinolone-, bedaquiline-, and linezolid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in China: Observations on surveillance data.J Infect Public Health. 2024 Jan;17(1):137-142. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2023.11.018. Epub 2023 Nov 21. J Infect Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38000314
-
[Study on the resistance of rifampicin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis to anti-tuberculosis drugs in group A].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2023 Nov 12;46(11):1110-1117. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20230804-00046. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37914422 Chinese.
-
A Narrative Review of Bedaquiline and Delamanid: New Arsenals Against Multidrug-Resistant and Extensively Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2024 Aug;38(15-16):e25091. doi: 10.1002/jcla.25091. J Clin Lab Anal. 2024. PMID: 39431709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring diagnostic methods for drug-resistant tuberculosis: A comprehensive overview.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2024 Sep;148:102522. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2024.102522. Epub 2024 May 31. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2024. PMID: 38850839 Review.
Cited by
-
Pre-extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis among multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients in Ethiopia: a laboratory-based surveillance study.IJID Reg. 2022 Aug 30;5:39-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2022.08.012. eCollection 2022 Dec. IJID Reg. 2022. PMID: 36176268 Free PMC article.
-
Bedaquiline Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Rifampicin-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates in Zhejiang, China.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Oct 31;16:6951-6963. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S429003. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37928607 Free PMC article.
-
MycoVarP: Mycobacterium Variant and Drug Resistance Prediction Pipeline for Whole-Genome Sequence Data Analysis.Front Bioinform. 2022 Jun 3;1:805338. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2021.805338. eCollection 2021. Front Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 36303799 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant TB Among Smear-Positive Pulmonary TB Patients in Banadir, Somalia: A Multicenter Study.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Dec 10;15:7241-7248. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S386497. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36533250 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and Drug Resistance Patterns of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in High-Burden Area in Western Siberia, Russia.Microorganisms. 2023 Feb 8;11(2):425. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020425. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36838390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global tuberculosis report 2020. Geneva: WHO; 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources