Assessment of Salivary Cortisol Concentrations as a Level of Stress Indicator among Individuals Undergoing Dental Extraction Procedure
- PMID: 34447192
- PMCID: PMC8375931
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_557_20
Assessment of Salivary Cortisol Concentrations as a Level of Stress Indicator among Individuals Undergoing Dental Extraction Procedure
Abstract
Background: Anxious patients tend to exaggerate the aversive events before the actual dental therapy. The anxiety and fear are the major factors that regulate cortisol levels.
Aim: Our study aims to estimate the salivary cortisol among patients subjected to dental extraction and correlate any existence between pre- and post-extraction cortisol levels and vital parameters compared to the control group.
Methodology: The study sample included sixty individuals, thirty patients indicated for a dental extraction, and thirty healthy patients between the ages of 18 and 60 years. We collected saliva samples from the control group and pre- and post-extraction samples from the study group participants and vital parameters. We used quantitative ELISA Kit, Diagnostics Biochem Canada Inc. (DBC), to estimate the salivary cortisol level. We evaluated the values using the Chi-square test, Pearson correlation test, and paired t-test using the JMP 15; JMP Pro, Version 15 (SAS) Microsoft® Windows® for × 64.
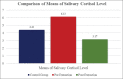
Results: The mean value of cortisol concentration of saliva was significantly greater in the preextraction group (6.13 ± 0.53 μg/dl) than after extraction group (3.17 ± 0.14 μg/dl) (P < 0.001). There were no significant associations between hemodynamic parameters and salivary cortisol concentration except for the postextraction systolic blood pressure (BP). A comparison of hemodynamic parameters between the study and control group revealed substantial differences in systolic BP.
Conclusion: The patient's anticipation and anxiety toward dental therapy elevate the cortisol level. Dental surgeons should treat the patients more conveniently and effectively without any strains and provide a comfortable atmosphere to avoid stress-related consequences.
Keywords: Dental extraction; salivary cortisol; stress fear.
Copyright: © 2021 Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Patil SJ, Shah PP, Patil JA, Shigli A, Patil AT, Tamagond SB. Assessment of the changes in the stress-related salivary cortisol levels to the various dental procedures in children. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2015;33:94–9. - PubMed
-
- Munck A, Guyre PM, Holbrook NJ. Physiological functions of glucocorticoids in stress and their relation to pharmacological actions. Endocr Rev. 1984;5:25–44. - PubMed
-
- Aardal E, Holm AC. Cortisol in saliva--reference ranges and relation to cortisol in serum. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1995;33:927–32. - PubMed
-
- Miller CS, Dembo JB, Falace DA, Kaplan AL. Salivary cortisol response to dental treatment of varying stress. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995;79:436–41. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources