Ludwig's angina in a COVID positive patient-An atypical case report
- PMID: 34448220
- PMCID: PMC8662242
- DOI: 10.1111/scd.12643
Ludwig's angina in a COVID positive patient-An atypical case report
Abstract
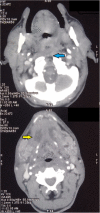
The management of odontogenic infections is established and several guidelines have been proposed for its effective treatment. Outbreak of COVID-19 has posed serious challenge in the management of odontogenic infections, further complicated by immunocompromised status of the patient, where adequate evaluation and prompt attention is mandatory to avoid untoward consequences. Ludwig's angina being a life threatening infection by itself, association or simultaneous presentation with COVID-19 infection can add further complexity in the management for a maxillofacial surgeon. Here we present a case report of Ludwig's angina in a patient who tested positive for Coronavirus infection and how we treated her successfully.
Keywords: COVID-19; Ludwig's angina; extraction; odontogenic infection.
© 2021 Special Care Dentistry Association and Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

