Tissue distribution of stem cell factor in adults
- PMID: 34450114
- PMCID: PMC8516741
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2021.104678
Tissue distribution of stem cell factor in adults
Abstract
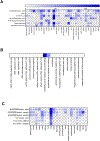
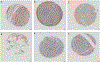
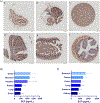
Stem cell factor (SCF) is an essential cytokine during development and is necessary for gametogenesis, hematopoiesis, mast cell development, stem cell function, and melanogenesis. Here, we measure SCF concentration and distribution in adult humans and mice using gene expression analysis, tissue staining, and organ protein lysates. We demonstrate continued SCF expression in many cell types and tissues into adulthood. Tissues with high expression in adult humans included stomach, spleen, kidney, lung, and pancreas. In mice, we found high SCF expression in the esophagus, ovary, uterus, kidney, and small intestine. Future studies may correlate our findings of increased, organ-specific SCF concentrations within adult tissues with increased risk of SCF/CD117-related disease.
Keywords: C-kit; CD117; Immunohistochemistry; Stem cell factor.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest, and the sponsors had no involvement in the design, collection, analysis, or interpretation of data nor in writing or submission of the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Sasaki T, Mizuochi C, Horio Y, Nakao K, Akashi K, Sugiyama D: Regulation of hematopoietic cell clusters in the placental niche through SCF/Kit signaling in embryonic mouse. J Cell Sci, The Company of Biologists, 2010, 123:e1.1–e1. - PubMed
-
- Ashman LK: The biology of stem cell factor and its receptor C-kit. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1999, 31:1037–1051. - PubMed
-
- Roskoski R: Signaling by Kit protein-tyrosine kinase - The stem cell factor receptor [Internet]. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2005. [cited 2017 Dec 19], pp. 1–13. Available from: https://ac.els-cdn.com/S0006291X05017596/1-s2.0-S0006291X05017596-main.p... - PubMed
-
- Broudy VC: Stem Cell Factor and Hematopoiesis. 1997. [cited 2018 Feb 22],. Available from: http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/bloodjournal/90/4/1345.full.pdf - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

