Matrix metalloproteinases are involved in the development of neurological complications in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019
- PMID: 34450402
- PMCID: PMC8367754
- DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108076
Matrix metalloproteinases are involved in the development of neurological complications in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019
Abstract
Background: Evidence show that Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) have been associated with neurological complications in the viral infections. Here in the current investigation, we intended to reveal if MMPs are potentially involved in the development of neurological symptoms in the patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Methods: The levels of MMPs, inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules were evaluated in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples from 10 COVID-19 patients with neurological syndrome (NS) and 10 COVID-19 patients lacking NS. Monocytes from the CSF samples were treated with TNF-α and the secreted levels of MMPs were determined.
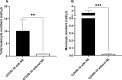
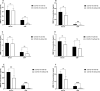
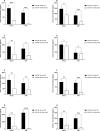
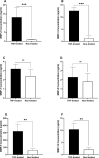
Results: The frequency of monocytes were increased in the CSF samples of COVID-19 patients with NS compared to patients without NS. Levels of inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, chemokines CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, CCL7, CCL12, CXCL8, and CX3CL1, MMPs MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-9, and MMP-12, and adhesion molecules ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E-selectin were significantly increased in the CSF samples of COVID-19 patients with NS compared with patients without NS. Treatment of CSF-derived monocytes obtained from COVID-19 patients with NS caused increased production of MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-9, and MMP-12.
Conclusions: Higher levels of inflammatory cytokines might promote the expression of adhesion molecules on blood-CSF barrier (BCSFB), resulting in facilitation of monocyte recruitment. Increased levels of CSF chemokines might also help to the trafficking of monocytes to CSF. Inflammatory cytokines might enhance production of MMPs from monocytes, leading to disruption of BCSFB (and therefore further infiltration of inflammatory cells to CSF) in COVID-19 patients with NS.
Keywords: Adhesion molecule; Chemokine; Coronavirus disease 2019; Inflammatory cytokine; Matrix metalloproteinases; Neurological symptom.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
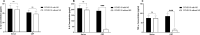

References
-
- Tabrizi Z.A., Khosrojerdi A., Aslani S., Hemmatzadeh M., Babaie F., Bairami A., Shomali N., Hosseinzadeh R., Safari R., Mohammadi H. Multi-facets of neutrophil extracellular trap in infectious diseases: Moving beyond immunity. Microb. Pathog. 2021;158 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

