Time-Course Transcriptome Profiling of a Poxvirus Using Long-Read Full-Length Assay
- PMID: 34451383
- PMCID: PMC8398953
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens10080919
Time-Course Transcriptome Profiling of a Poxvirus Using Long-Read Full-Length Assay
Abstract
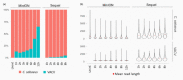
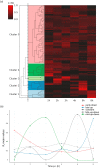
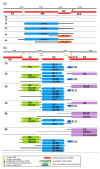
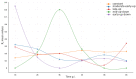
Viral transcriptomes that are determined using first- and second-generation sequencing techniques are incomplete. Due to the short read length, these methods are inefficient or fail to distinguish between transcript isoforms, polycistronic RNAs, and transcriptional overlaps and readthroughs. Additionally, these approaches are insensitive for the identification of splice and transcriptional start sites (TSSs) and, in most cases, transcriptional end sites (TESs), especially in transcript isoforms with varying transcript ends, and in multi-spliced transcripts. Long-read sequencing is able to read full-length nucleic acids and can therefore be used to assemble complete transcriptome atlases. Although vaccinia virus (VACV) does not produce spliced RNAs, its transcriptome has a high diversity of TSSs and TESs, and a high degree of polycistronism that leads to enormous complexity. We applied single-molecule, real-time, and nanopore-based sequencing methods to investigate the time-lapse transcriptome patterns of VACV gene expression.
Keywords: gene expression; long-read sequencing; nanopore sequencing; transcriptome profiling; vaccinia virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Moss B. Poxviridae. In: Knipe B.M., Howley P.M., Cohen J.I., Griffin D.E., Lamb R.A., Martin M.A., Rancaniello V.R., Roizman B., editors. Fields Virology. 6th ed. Volume 2. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2013. pp. 2129–2159.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

