Primary and Metastatic Brain Tumours Assessed with the Brain and Torso [18F]FDG PET/CT Study Protocol-10 Years of Single-Institutional Experiences
- PMID: 34451818
- PMCID: PMC8401235
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14080722
Primary and Metastatic Brain Tumours Assessed with the Brain and Torso [18F]FDG PET/CT Study Protocol-10 Years of Single-Institutional Experiences
Abstract
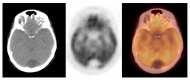
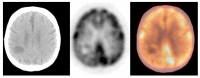
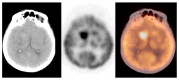
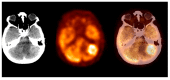
According to the international societies' recommendations, the 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography ([18F]FDG PET/CT) technique should not be used as the method of choice in brain tumour diagnosis. Therefore, the brain region can be omitted during standard [18F]FDG PET/CT scanning. We performed comprehensive literature research and analysed results from 14,222 brain and torso [18F]FDG PET/CT studies collected in 2010-2020. We found 131 clinically silent primary and metastatic brain tumours and 24 benign lesions. We concluded that the brain and torso [18F]FDG PET/CT study provides valuable data that may support therapeutic management by detecting clinically silent primary and metastatic brain tumours.
Keywords: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose; brain tumour; oncology; positron emission tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in brain tumours diagnosis.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2022 May 19;27(2):235-240. doi: 10.5603/RPOR.a2022.0021. eCollection 2022. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2022. PMID: 36299374 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of clinically silent brain lesions in [18F]FDG PET/CT study in oncological patients: analysis of over 10,000 studies.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 14;11(1):18293. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98004-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34521979 Free PMC article.
-
More advantages in detecting bone and soft tissue metastases from prostate cancer using 18F-PSMA PET/CT.Hell J Nucl Med. 2019 Jan-Apr;22(1):6-9. doi: 10.1967/s002449910952. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Hell J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30843003
-
18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in muscle-invasive bladder cancer.Curr Opin Urol. 2020 Sep;30(5):654-664. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0000000000000798. Curr Opin Urol. 2020. PMID: 32701719 Review.
-
Imaging in endocrinology: 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in differentiated thyroid carcinoma: clinical indications and controversies in diagnosis and follow-up.Eur J Endocrinol. 2015 Sep;173(3):R115-30. doi: 10.1530/EJE-15-0066. Epub 2015 May 6. Eur J Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25947140 Review.
References
-
- Stewart B.W., Wild C.P. Chapter 5.16. In: Kleihues P., Barnholtz-Sloan J., Ohgaki H., editors. World Cancer Report 2014. 1st ed. WHO Press; Geneva, Switzerland: 2015. pp. 511–520.
-
- National Brain Tumor Society. [(accessed on 1 April 2021)]; Available online: https://braintumor.org/brain-tumor-information/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

