Pitavastatin Is a Highly Potent Inhibitor of T-Cell Proliferation
- PMID: 34451823
- PMCID: PMC8399298
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14080727
Pitavastatin Is a Highly Potent Inhibitor of T-Cell Proliferation
Abstract
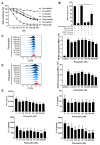
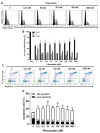
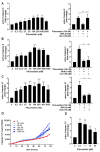
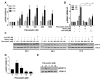
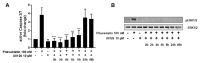
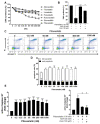
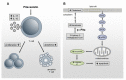
Repositioning of approved drugs is an alternative time- and cost-saving strategy to classical drug development. Statins are 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG CoA) reductase inhibitors that are usually used as cholesterol-lowering medication, and they also exhibit anti-inflammatory effects. In the present study, we observed that the addition of Pitavastatin at nanomolar concentrations inhibits the proliferation of CD3/CD28 antibody-stimulated human T cells of healthy donors in a dose-dependent fashion. The 50% inhibition of proliferation (IC50) were 3.6 and 48.5 nM for freshly stimulated and pre-activated T cells, respectively. In addition, Pitavastatin suppressed the IL-10 and IL-17 production of stimulated T cells. Mechanistically, we found that treatment of T cells with doses <1 µM of Pitavastatin induced hyperphosphorylation of ERK1/2, and activation of caspase-9, -3 and -7, thus leading to apoptosis. Mevalonic acid, cholesterol and the MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126 reversed this Pitavastatin-mediated ERK1/2 activation and apoptosis of T cells. In summary, our results suggest that Pitavastatin is a highly potent inhibitor of T-cell proliferation, which induces apoptosis via pro-apoptotic ERK1/2 activation, thus representing a potential repositioning candidate for the treatment of T-cell-mediated autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: ERK1/2 activation; Pitavastatin; apoptosis; drug repositioning; inhibitor of T-cell proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Screening of FDA-Approved Drug Library Identifies Adefovir Dipivoxil as Highly Potent Inhibitor of T Cell Proliferation.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 8;11:616570. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.616570. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33488629 Free PMC article.
-
MCP-1-induced enhancement of THP-1 adhesion to vascular endothelium was modulated by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor through RhoA GTPase-, but not ERK1/2-dependent pathway.Life Sci. 2004 Jul 30;75(11):1333-41. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.02.028. Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15234191
-
Pitavastatin inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by inactivating extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2003;10(1):37-42. doi: 10.5551/jat.10.37. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2003. PMID: 12621163
-
Pitavastatin: efficacy and safety profiles of a novel synthetic HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor.Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2003 Fall;21(3):199-215. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2003.tb00116.x. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2003. PMID: 12931254 Review.
-
[Effect of pitavastatin on macrophage cholesterol metabolism].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008 Mar;128(3):357-63. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.128.357. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008. PMID: 18311054 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Exploring a repurposed candidate with dual hIDO1/hTDO2 inhibitory potential for anticancer efficacy identified through pharmacophore-based virtual screening and in vitro evaluation.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 24;14(1):9386. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59353-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38653790 Free PMC article.
-
Statin drugs enhance responses to immune checkpoint blockade in head and neck cancer models.J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Jan;11(1):e005940. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005940. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36650022 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

