Chirality-Dependent Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Glutathione after Spinal Cord Injury in an Animal Model
- PMID: 34451889
- PMCID: PMC8398565
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14080792
Chirality-Dependent Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Glutathione after Spinal Cord Injury in an Animal Model
Abstract
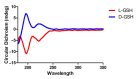
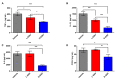
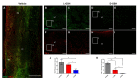
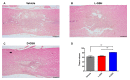
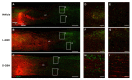
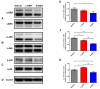
Neuroinflammation forms a glial scar following a spinal cord injury (SCI). The injured axon cannot regenerate across the scar, suggesting permanent paraplegia. Molecular chirality can show an entirely different bio-function by means of chiral-specific interaction. In this study, we report that d-chiral glutathione (D-GSH) suppresses the inflammatory response after SCI and leads to axon regeneration of the injured spinal cord to a greater extent than l-chiral glutathione (L-GSH). After SCI, axon regrowth in D-GSH-treated rats was significantly increased compared with that in L-GSH-treated rats (*** p < 0.001). Secondary damage and motor function were significantly improved in D-GSH-treated rats compared with those outcomes in L-GSH-treated rats (** p < 0.01). Moreover, D-GSH significantly decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) via inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway compared with L-GSH (*** p < 0.001). In primary cultured macrophages, we found that D-GSH undergoes more intracellular interaction with activated macrophages than L-GSH (*** p < 0.001). These findings reveal a potential new regenerative function of chiral GSH in SCI and suggest that chiral GSH has therapeutic potential as a treatment of other diseases.
Keywords: chirality; glial scars; glutathione; neuroinflammation; spinal cord injuries.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

