Single-Dose Intranasal Administration of AdCOVID Elicits Systemic and Mucosal Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 and Fully Protects Mice from Lethal Challenge
- PMID: 34452006
- PMCID: PMC8402488
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9080881
Single-Dose Intranasal Administration of AdCOVID Elicits Systemic and Mucosal Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 and Fully Protects Mice from Lethal Challenge
Abstract
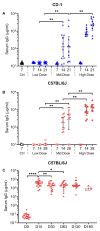
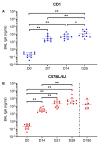
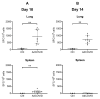
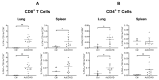
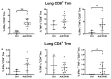
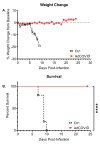
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has highlighted the urgent need for effective prophylactic vaccination to prevent the spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Intranasal vaccination is an attractive strategy to prevent COVID-19 as the nasal mucosa represents the first-line barrier to SARS-CoV-2 entry. The current intramuscular vaccines elicit systemic immunity but not necessarily high-level mucosal immunity. Here, we tested a single intranasal dose of our candidate adenovirus type 5-vectored vaccine encoding the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (AdCOVID) in inbred, outbred, and transgenic mice. A single intranasal vaccination with AdCOVID elicited a strong and focused immune response against RBD through the induction of mucosal IgA in the respiratory tract, serum neutralizing antibodies, and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells with a Th1-like cytokine expression profile. A single AdCOVID dose resulted in immunity that was sustained for over six months. Moreover, a single intranasal dose completely protected K18-hACE2 mice from lethal SARS-CoV-2 challenge, preventing weight loss and mortality. These data show that AdCOVID promotes concomitant systemic and mucosal immunity and represents a promising vaccine candidate.
Keywords: COVID-19; IgA; SARS-CoV-2; adenovirus vector; intranasal; mucosal immunity; receptor binding domain; vaccine; viral vector.
Conflict of interest statement
Investigators at The University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB: F.E.L. as project lead) and St. Louis University (SLU: J.D.B. as project lead) were funded by a sponsored research agreement from Altimmune to perform these studies. F.E.L., R.G.K. and T.D.R. serve as paid consultants for Altimmune. B.G., S.R., J.J.S., T.F., Y.L., B.S., V.K., I.P. and J.Z. are employees of Altimmune Inc. and may have received stock options and compensation as part of their employment. All other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Update of
-
Single-dose intranasal administration of AdCOVID elicits systemic and mucosal immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Oct 11:2020.10.10.331348. doi: 10.1101/2020.10.10.331348. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Aug 09;9(8):881. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9080881. PMID: 33052351 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) [(accessed on 5 October 2020)]; Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- CDC Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)—Scientific Brief: SARS-CoV-2 and Potential Airborne Transmission. [(accessed on 5 October 2020)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/more/scientific-brief-sars-cov....
-
- CDC Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): People Who Are at Increased Risk for Severe Illness. [(accessed on 4 August 2020)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

