Targeted Liposomes Encapsulating miR-603 Complexes Enhance Radiation Sensitivity of Patient-Derived Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells
- PMID: 34452076
- PMCID: PMC8399469
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081115
Targeted Liposomes Encapsulating miR-603 Complexes Enhance Radiation Sensitivity of Patient-Derived Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells
Abstract
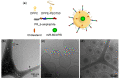
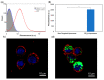
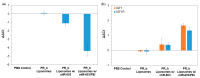
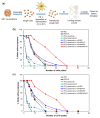
Despite potential for clinical efficacy, therapeutic delivery of microRNAs (miRNA) remains a major translational barrier. Here, we explore a strategy for miRNA delivery in the treatment of glioblastoma, the most common form of adult brain cancer, that involves complexation of miRNA with polyethylenimine (PEI) and encapsulation in targeted liposomes. miRNA 603 (miR-603) is a master regulatory miRNA that suppresses glioblastoma radiation resistance through down-regulation of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) signaling. miR-603 was complexed with PEI, a cationic polymer, and encapsulated into liposomes decorated with polyethylene glycol (PEG) and PR_b, a fibronectin-mimetic peptide that specifically targets the α5β1 integrin that is overexpressed in glioblastomas. Cultured patient-derived glioblastoma cells internalized PR_b-functionalized liposomes but not the non-targeted liposomes. The integrin targeting and complexation of the miRNA with PEI were associated with a 22-fold increase in intracellular miR-603 levels, and corresponding decreases in IGF1 and IGF1 receptor (IGF1R) mRNA expression. Moreover, treatment of glioblastoma cells with the PR_b liposomes encapsulating miR-603/PEI sensitized the cells to ionizing radiation (IR), a standard of care treatment for glioblastomas. These results suggest that PR_b-functionalized PEGylated liposomes encapsulating miR-603/PEI complexes hold promise as a therapeutic platform for glioblastomas.
Keywords: glioblastoma stem-cell state; miR-603; microRNA delivery; radiation therapy; stealth liposomes; targeting integrin α5β1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin targeted to α5β1-expressing MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.Langmuir. 2012 Mar 13;28(10):4729-36. doi: 10.1021/la204466g. Epub 2012 Feb 29. Langmuir. 2012. PMID: 22268611
-
PR_b-targeted PEGylated liposomes for prostate cancer therapy.Langmuir. 2008 Dec 2;24(23):13518-24. doi: 10.1021/la801961r. Langmuir. 2008. PMID: 18954096
-
Targeting HPV-infected cervical cancer cells with PEGylated liposomes encapsulating siRNA and the role of siRNA complexation with polyethylenimine.Bioeng Transl Med. 2016 Aug 8;1(2):168-180. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10022. eCollection 2016 Jun. Bioeng Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 29313012 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting colon cancer cells using PEGylated liposomes modified with a fibronectin-mimetic peptide.Int J Pharm. 2009 Jan 21;366(1-2):201-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.09.016. Epub 2008 Sep 19. Int J Pharm. 2009. PMID: 18835580 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: a review.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013 Nov;85(3 Pt A):427-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013. PMID: 23872180 Review.
Cited by
-
Polyethyleneimine-Based Lipopolyplexes as Carriers in Anticancer Gene Therapies.Materials (Basel). 2021 Dec 27;15(1):179. doi: 10.3390/ma15010179. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35009324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered smart materials for RNA based molecular therapy to treat Glioblastoma.Bioact Mater. 2023 Nov 27;33:396-423. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.11.007. eCollection 2024 Mar. Bioact Mater. 2023. PMID: 38059120 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of DNMT3A Attenuates the Warburg Effect, Proliferation, and Invasion via Promoting the Inhibition of miR-603 on HK2 in Ovarian Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15330338221110668. doi: 10.1177/15330338221110668. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 35770296 Free PMC article.
-
Status Quo in the Liposome-Based Therapeutic Strategies Against Glioblastoma: "Targeting the Tumor and Tumor Microenvironment".Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 19;25(20):11271. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011271. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Liposomes: A Nonviral Gene Delivery System for Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Apr 8;14(4):821. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040821. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35456655 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ramakrishnan V., Xu B., Akers J., Nguyen T., Ma J., Dhawan S., Ning J., Mao Y., Hua W., Kokkoli E., et al. Radiation-induced extracellular vesicle (EV) release of miR-603 promotes IGF1-mediated stem cell state in glioblastomas. EBioMedicine. 2020;55:102736. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102736. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

