Preparation of Magnetic-Luminescent Bifunctional Rapeseed Pod-Like Drug Delivery System for Sequential Release of Dual Drugs
- PMID: 34452077
- PMCID: PMC8398606
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081116
Preparation of Magnetic-Luminescent Bifunctional Rapeseed Pod-Like Drug Delivery System for Sequential Release of Dual Drugs
Abstract
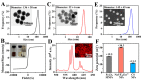
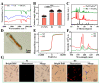
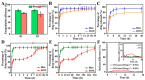
Drug delivery systems (DDSs) limited to a single function or single-drug loading are struggling to meet the requirements of clinical medical applications. It is of great significance to fabricate DDSs with multiple functions such as magnetic targeting or fluorescent labeling, as well as with multiple-drug loading for enhancing drug efficacy and accelerating actions. In this study, inspired by the dual-chamber structure of rapeseed pods, biomimetic magnetic-luminescent bifunctional drug delivery carriers (DDCs) of 1.9 ± 0.3 μm diameter and 19.6 ± 4.4 μm length for dual drug release were fabricated via double-needle electrospraying. Morphological images showed that the rapeseed pod-like DDCs had a rod-like morphology and Janus dual-chamber structure. Magnetic nanoparticles and luminescent materials were elaborately designed to be dispersed in two different chambers to endow the DDCs with excellent magnetic and luminescent properties. Synchronously, the Janus structure of DDCs promoted the luminescent intensity by at least threefold compared to single-chamber DDCs. The results of the hemolysis experiment and cytotoxicity assay suggested the great blood and cell compatibilities of DDCs. Further inspired by the core-shell structure of rapeseeds containing oil wrapped in rapeseed pods, DDCs were fabricated to carry benzimidazole molecules and doxorubicin@chitosan nanoparticles in different chambers, realizing the sequential release of benzimidazole within 12 h and of doxorubicin from day 3 to day 18. These rapeseed pod-like DDSs with excellent magnetic and luminescent properties and sequential release of dual drugs have potential for biomedical applications such as targeted drug delivery, bioimaging, and sustained treatment of diseases.
Keywords: dual drugs; electrospray; magnetic–luminescent bifunctional drug delivery carrier; rapeseed pod-like drug delivery system; sequential release.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Electrospun upconversion composite fibers as dual drugs delivery system with individual release properties.Langmuir. 2013 Jul 30;29(30):9473-82. doi: 10.1021/la402080y. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Langmuir. 2013. PMID: 23855606
-
Dual drug release from core-shell nanoparticles with distinct release profiles.J Pharm Sci. 2014 Oct;103(10):3205-16. doi: 10.1002/jps.24116. Epub 2014 Aug 12. J Pharm Sci. 2014. PMID: 25116645
-
A targeted drug delivery system based on folic acid-functionalized upconversion luminescent nanoparticles.J Biomater Appl. 2017 Apr;31(9):1247-1256. doi: 10.1177/0885328217701289. Epub 2017 Mar 28. J Biomater Appl. 2017. PMID: 28350205
-
Tailor made magnetic nanolights: fabrication to cancer theranostics applications.Nanoscale Adv. 2021 Oct 25;3(24):6762-6796. doi: 10.1039/d1na00447f. eCollection 2021 Dec 7. Nanoscale Adv. 2021. PMID: 36132370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carrageenan: A Wonder Polymer from Marine Algae for Potential Drug Delivery Applications.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(11):1172-1186. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190425190754. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 31465278 Review.
Cited by
-
Highly oriented hydrogels for tissue regeneration: design strategies, cellular mechanisms, and biomedical applications.Theranostics. 2024 Feb 24;14(5):1982-2035. doi: 10.7150/thno.89493. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38505623 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kohane D.S., Langer R. Biocompatibility and drug delivery systems. Chem. Sci. 2010;1:441–446. doi: 10.1039/C0SC00203H. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

