Characterization of the Roles of SGT1/RAR1, EDS1/NDR1, NPR1, and NRC/ADR1/NRG1 in Sw-5b-Mediated Resistance to Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus
- PMID: 34452313
- PMCID: PMC8402918
- DOI: 10.3390/v13081447
Characterization of the Roles of SGT1/RAR1, EDS1/NDR1, NPR1, and NRC/ADR1/NRG1 in Sw-5b-Mediated Resistance to Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus
Abstract
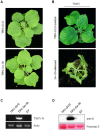
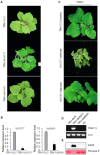
The tomato Sw-5b gene confers resistance to tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) and encodes a nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat (NLR) protein with an N-terminal Solanaceae-specific domain (SD). Although our understanding of how Sw-5b recognizes the viral NSm elicitor has increased significantly, the process by which Sw-5b activates downstream defense signaling remains to be elucidated. In this study, we used a tobacco rattle virus (TRV)-based virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) system to investigate the roles of the SGT1/RAR1, EDS1/NDR1, NPR1, and NRC/ADR1/NRG1 genes in the Sw-5b-mediated signaling pathway. We found that chaperone SGT1 was required for Sw-5b function, but co-chaperone RAR1 was not. Sw-5b-mediated immune signaling was independent of both EDS1 and NDR1. Silencing NPR1, which is a central component in SA signaling, did not result in TSWV systemic infection in Sw-5b-transgenic N. benthamiana plants. Helper NLR NRCs (NLRs required for cell death) were required for Sw-5b-mediated systemic resistance to TSWV infection. Suppression of NRC2/3/4 compromised the Sw-5b resistance. However, the helper NLRs ADR1 and NRG1 may not participate in the Sw-5b signaling pathway. Silencing ADR1, NRG1, or both genes did not affect Sw-5b-mediated resistance to TSWV. Our findings provide new insight into the requirement for conserved key components in Sw-5b-mediated signaling pathways.
Keywords: NLR receptor; Sw-5b; defense signaling; plant innate immunity; tomato spotted wilt virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Natural Resources Resistance to Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus (TSWV) in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum).Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 12;22(20):10978. doi: 10.3390/ijms222010978. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell death triggering and effector recognition by Sw-5 SD-CNL proteins from resistant and susceptible tomato isolines to Tomato spotted wilt virus.Mol Plant Pathol. 2016 Dec;17(9):1442-1454. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12439. Epub 2016 Aug 14. Mol Plant Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27271212 Free PMC article.
-
The NSm proteins of phylogenetically related tospoviruses trigger Sw-5b-mediated resistance dissociated of their cell-to-cell movement function.Virus Res. 2017 Aug 15;240:25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2017.07.019. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 28754561
-
The Tomato spotted wilt virus cell-to-cell movement protein (NSM ) triggers a hypersensitive response in Sw-5-containing resistant tomato lines and in Nicotiana benthamiana transformed with the functional Sw-5b resistance gene copy.Mol Plant Pathol. 2014 Dec;15(9):871-80. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12144. Epub 2014 May 11. Mol Plant Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24720811 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Sw5 Gene Cluster in the Fight against Plant Viruses.J Virol. 2022 Mar 9;96(5):e0208421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02084-21. Epub 2022 Jan 5. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34985996 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in understanding the interaction between Solanaceae NLR resistance proteins and the viral effector Avr.Plant Signal Behav. 2024 Dec 31;19(1):2382497. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2024.2382497. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Plant Signal Behav. 2024. PMID: 39312190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Resources Resistance to Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus (TSWV) in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum).Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 12;22(20):10978. doi: 10.3390/ijms222010978. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A conserved protein disulfide isomerase enhances plant resistance against herbivores.Plant Physiol. 2023 Jan 2;191(1):660-678. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac489. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36269175 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the genetic basis of quantitative resistance to diseases in tomato: a meta-QTL analysis and mining of transcript profiles.Plant Cell Rep. 2024 Jul 1;43(7):184. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03268-x. Plant Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38951262
-
The Hypersensitive Response to Plant Viruses.Viruses. 2023 Sep 26;15(10):2000. doi: 10.3390/v15102000. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37896777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

