Strategies to Optimise Oncolytic Viral Therapies: The Role of Natural Killer Cells
- PMID: 34452316
- PMCID: PMC8402671
- DOI: 10.3390/v13081450
Strategies to Optimise Oncolytic Viral Therapies: The Role of Natural Killer Cells
Abstract
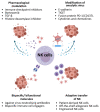
Oncolytic viruses (OVs) are an emerging class of anti-cancer agents that replicate selectively within malignant cells and generate potent immune responses. Their potential efficacy has been shown in clinical trials, with talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC or IMLYGIC®) now approved both in the United States and Europe. In healthy individuals, NK cells provide effective surveillance against cancer and viral infections. In oncolytic viral therapy, NK cells may render OV ineffective by rapid elimination of the propagating virus but could also improve therapeutic efficacy by preferential killing of OV-infected malignant cells. Existing evidence suggests that the overall effect of NK cells against OV is context dependent. In the past decade, the understanding of cancer and OV biology has improved significantly, which helped refine this class of treatments in early-phase clinical trials. In this review, we summarised different strategies that have been evaluated to modulate NK activities for improving OV therapeutic benefits. Further development of OVs will require a systematic approach to overcome the challenges of the production and delivery of complex gene and cell-based therapies in clinical settings.
Keywords: NK cells; gene therapy; immunotherapy; neoplasms; oncolytic virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oncolytic virotherapy as promising immunotherapy against cancer: mechanisms of resistance to oncolytic viruses.Future Oncol. 2022 Jan;18(2):245-259. doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-0802. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Future Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34821517 Review.
-
The two-faces of NK cells in oncolytic virotherapy.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020 Dec;56:59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.06.005. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020. PMID: 32586674 Review.
-
The discovery and development of oncolytic viruses: are they the future of cancer immunotherapy?Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2021 Apr;16(4):391-410. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2021.1850689. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 33232188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New hopes for the breast cancer treatment: perspectives on the oncolytic virus therapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 21;15:1375433. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1375433. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38576614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncolytic Viruses in Cancer Treatment: A Review.JAMA Oncol. 2017 Jun 1;3(6):841-849. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.2064. JAMA Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27441411 Review.
Cited by
-
Oncolytic viruses improve cancer immunotherapy by reprogramming solid tumor microenvironment.Med Oncol. 2023 Dec 8;41(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02233-0. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38062315 Review.
-
Multiomic Profiling Identified EGF Receptor Signaling as a Potential Inhibitor of Type I Interferon Response in Models of Oncolytic Therapy by Vesicular Stomatitis Virus.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 8;23(9):5244. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095244. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andtbacka R.H.I., Kaufman H.L., Collichio F., Amatruda T., Senzer N., Chesney J., Delman K.A., Spitler L.E., Puzanov I., Agarwala S.S., et al. Talimogene Laherparepvec improves durable response rate in patients with advanced melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015 doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.3377. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

