Animal Coronavirus Diseases: Parallels with COVID-19 in Humans
- PMID: 34452372
- PMCID: PMC8402828
- DOI: 10.3390/v13081507
Animal Coronavirus Diseases: Parallels with COVID-19 in Humans
Abstract
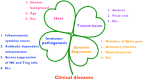
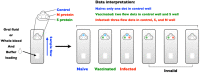
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), a novel coronavirus in humans, has expanded globally over the past year. COVID-19 remains an important subject of intensive research owing to its huge impact on economic and public health globally. Based on historical archives, the first coronavirus-related disease recorded was possibly animal-related, a case of feline infectious peritonitis described as early as 1912. Despite over a century of documented coronaviruses in animals, the global animal industry still suffers from outbreaks. Knowledge and experience handling animal coronaviruses provide a valuable tool to complement our understanding of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. In this review, we present an overview of coronaviruses, clinical signs, COVID-19 in animals, genome organization and recombination, immunopathogenesis, transmission, viral shedding, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. By drawing parallels between COVID-19 in animals and humans, we provide perspectives on the pathophysiological mechanisms by which coronaviruses cause diseases in both animals and humans, providing a critical basis for the development of effective vaccines and therapeutics against these deadly viruses.
Keywords: COVID-19; DIVA; animal coronavirus; immunopathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Woo P.C., Lau S.K., Lam C.S., Lau C.C., Tsang A.K., Lau J.H., Bai R., Teng J.L., Tsang C.C., Wang M., et al. Discovery of seven novel Mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012;86:3995–4008. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jakob H. Therapeutsiche, kasuisitische und statistische Mitteilungen aus der Klinik für kleine Haustiere an der Reichstierarzneischule in Utrecht (Holland), Jahrgang 1912/13. Z Tiermed. Microbiol. Immunol. 1914;18:193.
-
- Schneider E. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Netter’s Infect. Dis. 2012:537–543. doi: 10.1016/B978-1-4377-0126-5.00089-6. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

