Endocrine disrupting chemicals and reproductive disorders in women, men, and animal models
- PMID: 34452686
- PMCID: PMC9743013
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.apha.2021.03.008
Endocrine disrupting chemicals and reproductive disorders in women, men, and animal models
Abstract
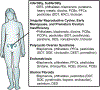
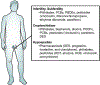
This chapter covers the known effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) on reproductive disorders. The EDCs represented are highly studied, including plasticizers (bisphenols and phthalates), chemicals in personal care products (parabens), persistent environmental contaminants (polychlorinated biphenyls), and chemicals in pesticides or herbicides. Both female and male reproductive disorders are reviewed in the chapter. Female disorders include infertility/subfertility, irregular reproductive cycles, early menopause, premature ovarian insufficiency, polycystic ovarian syndrome, endometriosis, and uterine fibroids. Male disorders include infertility/subfertility, cryptorchidism, and hypospadias. Findings from both human and animal studies are represented.
Keywords: Bisphenol; Endocrine disrupting chemical; Fertility; Paraben; Perfluorochemical; Pesticides; Phthalate; Polychlorinated biphenyls; Reproduction; Reproductive system health.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources