Lixisenatide is effective and safe as add-on treatment to basal insulin in Asian individuals with type 2 diabetes and different body mass indices: a pooled analysis of data from the GetGoal Studies
- PMID: 34452904
- PMCID: PMC8404431
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2021-002290
Lixisenatide is effective and safe as add-on treatment to basal insulin in Asian individuals with type 2 diabetes and different body mass indices: a pooled analysis of data from the GetGoal Studies
Abstract
Introduction: This analysis aims to investigate the efficacy and safety of once-daily lixisenatide add-on treatment to basal insulin in Asian individuals with type 2 diabetes, by baseline body mass index (BMI).
Research design and methods: Data from all Asian participants in the placebo-controlled GetGoal-Duo 1, GetGoal-L, and GetGoal-L-C Studies were pooled and categorized according to the following BMI subgroups:<25 kg/m2, 25-<30 kg/m2 and ≥30 kg/m2. Efficacy and safety of lixisenatide versus placebo were evaluated among BMI subgroups. Multivariable regression analyses were also conducted to explore the potential influence of BMI on efficacy outcomes after adjusting for baseline characteristics.
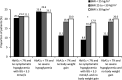
Results: 555 participants were included (mean age 53.9 years, 52.4% men). No significant differences in treatment effect between the BMI subgroups were observed for the changes from baseline to 24 weeks in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), fasting plasma glucose, postprandial glucose (PPG), PPG excursion, body weight, BMI, and basal insulin dose with lixisenatide, as well as the change in basal insulin dose at study endpoint and the proportion of participants achieving an HbA1c <7% at 24 weeks (all p values for interaction >0.15). In the multivariable regression analysis, participants in the lowest BMI group had a smaller reduction in body weight over the 24-week treatment period relative to the highest BMI group (p=0.023).
Conclusions: This post hoc analysis indicates that lixisenatide improved glycemic control regardless of baseline BMI and was well tolerated in Asian individuals unable to achieve their HbA1c target on basal insulin±oral antidiabetic drugs.
Keywords: body mass index; diabetes mellitus; glucagon-like peptide 1; type 2.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: WF, WW, RM and DZ declare no conflict of interest. GW, MZ, XZ and HY are employees of Sanofi China.
Figures
References
-
- Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, et al. . 2019 update to: management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American diabetes association (ADA) and the European association for the study of diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2020;43:487–93. 10.2337/dci19-0066 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical