Maternal speech decreases pain scores and increases oxytocin levels in preterm infants during painful procedures
- PMID: 34453088
- PMCID: PMC8397753
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-96840-4
Maternal speech decreases pain scores and increases oxytocin levels in preterm infants during painful procedures
Abstract
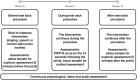
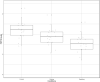
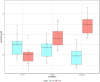
Preterm infants undergo early separation from parents and are exposed to frequent painful clinical procedures, with resultant short- and long-term effects on their neurodevelopment. We aimed to establish whether the mother's voice could provide an effective and safe analgesia for preterm infants and whether endogenous oxytocin (OXT) could be linked to pain modulation. Twenty preterm infants were exposed to three conditions-mother's live voice (speaking or singing) and standard care-in random order during a painful procedure. OXT levels (pg/mL) in saliva and plasma cortisol levels were quantified, and the Premature Infant Pain Profile (PIPP) was blindly coded by trained psychologists. During the mother's live voice, PIPP scores significantly decreased, with a concomitant increase in OXT levels over baseline. The effect on pain perception was marginally significant for singing. No effects on cortisol levels were found. The mother's live voice modulated preterm infants' pain indicators. Endogenous OXT released during vocal contact is a promising protective mechanism during early painful interventions in at-risk populations.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Born Too Soon: The Global Action Report on Preterm Birth. (2012).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

