Cycle Length Evaluation in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Using Kernel Density Estimation to Identify Transient and Stable Rapid Atrial Activity
- PMID: 34453278
- PMCID: PMC9114079
- DOI: 10.1007/s13239-021-00568-1
Cycle Length Evaluation in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Using Kernel Density Estimation to Identify Transient and Stable Rapid Atrial Activity
Abstract
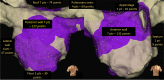
Purpose: Left atrial (LA) rapid AF activity has been shown to co-localise with areas of successful atrial fibrillation termination by catheter ablation. We describe a technique that identifies rapid and regular activity.
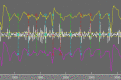
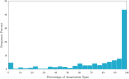
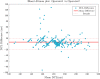
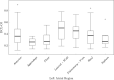
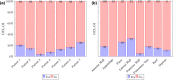
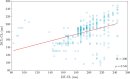
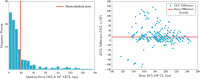
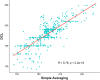
Methods: Eight-second AF electrograms were recorded from LA regions during ablation for psAF. Local activation was annotated manually on bipolar signals and where these were of poor quality, we inspected unipolar signals. Dominant cycle length (DCL) was calculated from annotation pairs representing a single activation interval, using a probability density function (PDF) with kernel density estimation. Cumulative annotation duration compared to total segment length defined electrogram quality. DCL results were compared to dominant frequency (DF) and averaging.
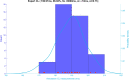
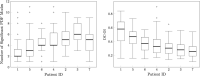
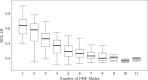
Results: In total 507 8 s AF segments were analysed from 7 patients. Spearman's correlation coefficient was 0.758 between independent annotators (P < 0.001), 0.837-0.94 between 8 s and ≥ 4 s segments (P < 0.001), 0.541 between DCL and DF (P < 0.001), and 0.79 between DCL and averaging (P < 0.001). Poorer segment organization gave greater errors between DCL and DF.
Conclusion: DCL identifies rapid atrial activity that may represent psAF drivers. This study uses DCL as a tool to evaluate the dynamic, patient specific properties of psAF by identifying rapid and regular activity. If automated, this technique could rapidly identify areas for ablation in psAF.
Keywords: Ablation; Biomedical signal processing; Cardiology; Extra pulmonary vein drivers; Intracardiac electrograms.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Kasi, Afonso, Bird, Pederson, Kim are employees of Abbott, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Atienza F, Almendral J, Ormaetxe JM, Moya Á, Martínez-Alday JD, Hernández-Madrid A, Castellanos E, Arribas F, Arias MÁ, Tercedor L, Peinado R, Fe Arcocha M, Ortiz M, Martínez-Alzamora N, Arenal Á, Fernández-Avilés F, Jalife J. Comparison of radiofrequency catheter ablation of drivers and circumferential pulmonary vein isolation in atrial fibrillation: A noninferiority randomized multicenter RADAR-AF trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014;64:2455–2467. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.09.053. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cappato R, Calkins H, Chen S, Davies W, Iesaka Y, Kalman J, Kim Y, Klein G, Natale A, Packer D, Skanes A, Ambrogi F, Biganzoli E. Updated worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2010;3:32–38. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.109.859116. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

