Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease improves detection of high liver stiffness: The Rotterdam Study
- PMID: 34453359
- PMCID: PMC9299928
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.32131
Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease improves detection of high liver stiffness: The Rotterdam Study
Abstract
Background and aims: Recently metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) has been introduced and was defined as hepatic steatosis with either overweight, diabetes, and/or a combination of other metabolic risk factors. We investigated the application of the MAFLD criteria as compared with NAFLD.
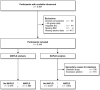
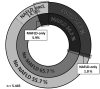
Approach and results: We performed a cross-sectional analysis within the Rotterdam Study, a large prospective population-based cohort. Participants who attended the liver ultrasound and transient elastography program between 2009 and 2014 were eligible for inclusion. Subsequently, individuals with viral hepatitis, alcohol intake >60 g/day, missing alcohol data, and/or missing body mass index were excluded. According to their NAFLD and MAFLD status based on metadata and ultrasound, participants were allocated in overlap fatty liver disease (FLD), NAFLD-only, MAFLD-only, or no FLD. Fibrosis was defined as liver stiffness ≥8.0 kPa. In our analysis, 5445 participants were included: 1866 (34.3%) had MAFLD and 1604 (29.5%) [Correction added on December 27, 2021 after first online publication: The preceding fragment was changed from "1623 (29.8%)"] had NAFLD. This resulted in 1547 (28.4%) [Correction added on December 27, 2021 after first online publication: The preceding fragment was changed from "1566 (28.8%)"] individuals with overlap FLD, 319 (5.9%) [Correction added on December 27, 2021 after first online publication: The preceding fragment was changed from "300 (5.5%)"] with MAFLD-only, 57 (1.0%) with NAFLD-only, and 3522 (64.7%) with no FLD. The MAFLD-only group was strongly associated with fibrosis (adjusted OR 5.30 [Correction added on December 27, 2021 after first online publication: The preceding fragment was changed from "OR 5.27"], p < 0.001) and log-transformed liver stiffness (adjusted beta 0.116, p < 0.001), as opposed to the NAFLD-only group, in which no cases of fibrosis were identified and no association with liver stiffness (adjusted beta 0.006, p = 0.90) was found.
Conclusions: FLD is highly prevalent in the general population. However, not the NAFLD-only, but the MAFLD-only group was associated with fibrosis and higher liver stiffness-independent of demographic and lifestyle factors. We believe that using the MAFLD criteria will help improve the identification and treatment of patients with FLD at risk for fibrosis.
© 2021 The Authors. Hepatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. de Knegt consults and received grants from AbbVie. He is on the speakers’ bureau for Echosens. He received grants from Gilead and Janssen.
Figures
References
-
- Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—meta‐analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73–84. - PubMed
-
- Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, Hardy T, Henry L, Eslam M, et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Engin A. The definition and prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Labenz C, Huber Y, Michel M, Nagel M, Galle PR, Kostev K, et al. Impact of NAFLD on the incidence of cardiovascular diseases in a primary care population in germany. Dig Dis Sci. 2020;65:2112–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

