Functional validation of pathogenicity genes in rice sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia solani by a novel host-induced gene silencing system
- PMID: 34453407
- PMCID: PMC8578826
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.13130
Functional validation of pathogenicity genes in rice sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia solani by a novel host-induced gene silencing system
Abstract
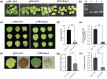
Rice sheath blight, caused by the soilborne fungus Rhizoctonia solani, causes severe yield losses worldwide. Elucidation of the pathogenic mechanism of R. solani is highly desired. However, the lack of a stable genetic transformation system has made it challenging to examine genes' functions in this fungus. Here, we present functional validation of pathogenicity genes in the rice sheath blight pathogen R. solani by a newly established tobacco rattle virus (TRV)-host-induced gene silencing (HIGS) system using the virulent R. solani AG-1 IA strain GD-118. RNA interference constructs of 33 candidate pathogenicity genes were infiltrated into Nicotiana benthamiana leaves with the TRV-HIGS system. Of these constructs, 29 resulted in a significant reduction in necrosis caused by GD-118 infection. For further validation of one of the positive genes, trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase (Rstps2), stable rice transformants harbouring the double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) construct for Rstps2 were created. The transformants exhibited reduced gene expression of Rstps2, virulence, and trehalose accumulation in GD-118. We showed that the dsRNA for Rstps2 was taken up by GD-118 mycelia and sclerotial differentiation of GD-118 was inhibited. These findings offer gene identification opportunities for the rice sheath blight pathogen and a theoretical basis for controlling this disease by spray-induced gene silencing.
Keywords: Rhizoctonia solani; host-induced gene silencing; pathogenicity gene; rice disease control strategy; rice sheath blight.
© 2021 The Authors. Molecular Plant Pathology published by British Society for Plant Pathology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pectin induced transcriptome of a Rhizoctonia solani strain causing sheath blight disease in rice reveals insights on key genes and RNAi machinery for development of pathogen derived resistance.Plant Mol Biol. 2019 May;100(1-2):59-71. doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00843-9. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Plant Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30796712
-
Molecular Characterization of a Novel Endornavirus Conferring Hypovirulence in Rice Sheath Blight Fungus Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA Strain GD-2.Viruses. 2019 Feb 20;11(2):178. doi: 10.3390/v11020178. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30791630 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and expression analysis of pathogenicity-related genes of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis groups infecting rice.3 Biotech. 2021 Aug;11(8):394. doi: 10.1007/s13205-021-02934-1. Epub 2021 Aug 2. 3 Biotech. 2021. PMID: 34458063 Free PMC article.
-
Rhizoctonia solani Kühn Pathophysiology: Status and Prospects of Sheath Blight Disease Management in Rice.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 3;13:881116. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.881116. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35592572 Free PMC article.
-
Sheath blight of rice: a review and identification of priorities for future research.Planta. 2019 Nov;250(5):1387-1407. doi: 10.1007/s00425-019-03246-8. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Planta. 2019. PMID: 31346804 Review.
Cited by
-
Host induced gene silencing of Magnaporthe oryzae by targeting pathogenicity and development genes to control rice blast disease.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 11;13:959641. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.959641. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36035704 Free PMC article.
-
Why Do We Need Alternative Methods for Fungal Disease Management in Plants?Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 10;12(22):3822. doi: 10.3390/plants12223822. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative genomics and transcriptomics identify Rhizoctonia solani AG-7 cytochrome P450 gene RsCYP-1 for pencycuron resistance.iScience. 2025 May 26;28(7):112756. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112756. eCollection 2025 Jul 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40585356 Free PMC article.
-
The host and pathogen myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthases are required for Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA infection in tomato.Mol Plant Pathol. 2024 Oct;25(10):e13470. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13470. Mol Plant Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39376048 Free PMC article.
-
SsUbc2, a determinant of pathogenicity, functions as a key coordinator controlling global transcriptomic reprogramming during mating in sugarcane smut fungus.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 20;13:954767. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.954767. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36204604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson, J.P. , Hane, J.K. , Stoll, T. , Pain, N. , Hastie, M.L. , Kaur, P. et al. (2016) Proteomic analysis of Rhizoctonia solani identifies infection‐specific, redox associated proteins and insight into adaptation to different plant hosts. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 15, 1188–1203. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cao, Y. , Wang, Y. , Dai, B.D. , Wang, B. , Zhang, H. , Zhu, Z. et al. (2008) Trehalose is an important mediator of cap1p oxidative stress response in Candida albicans . Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 31, 421–425. - PubMed
-
- Cervantes‐Chávez, J.A. , Valdés‐Santiago, L. , Bakkeren, G. , Hurtado‐Santiago, E. , León‐Ramírez, C.G. , Esquivel‐Naranjo, E.U. et al. (2016) Trehalose is required for stress resistance and virulence of the basidiomycota plant pathogen Ustilago maydis . Microbiology, 162, 1009–1022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

