KCTD11 inhibits progression of lung cancer by binding to β-catenin to regulate the activity of the Wnt and Hippo pathways
- PMID: 34453479
- PMCID: PMC8500973
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16883
KCTD11 inhibits progression of lung cancer by binding to β-catenin to regulate the activity of the Wnt and Hippo pathways
Abstract
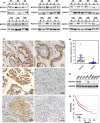
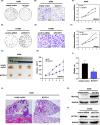
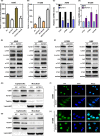
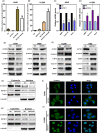
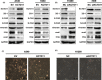
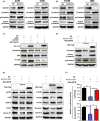
KCTD11 has been reported to be a potential tumour suppressor in several tumour types. However, the expression of KCTD11 and its role has not been reported in human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Whether its potential molecular mechanism is related to its BTB domain is also unknown. The expression of KCTD11 in 139 NSCLC tissue samples was detected by immunohistochemistry, and its correlation with clinicopathological factors was analysed. The effect of KCTD11 on the biological behaviour of lung cancer cells was verified in vitro and in vivo. Its effect on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition(EMT)process and the Wnt/β-catenin and Hippo/YAP pathways were observed by Western blot, dual-luciferase assay, RT-qPCR, immunofluorescence and immunoprecipitation. KCTD11 is under-expressed in lung cancer tissues and cells and was negatively correlated with the degree of differentiation, tumour-node-metastasis (TNM) stage and lymph node metastasis. Low KCTD11 expression was associated with poor prognosis. KCTD11 overexpression inhibited the proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells. Further studies indicated that KCTD11 inhibited the Wnt pathway, activated the Hippo pathway and inhibited EMT processes by inhibiting the nuclear translocation of β-catenin and YAP. KCTD11 lost its stimulatory effect on the Hippo pathway after knock down of β-catenin. These findings confirm that KCTD11 inhibits β-catenin and YAP nuclear translocation as well as the malignant phenotype of lung cancer cells by interacting with β-catenin. This provides an important experimental basis for the interaction between KCTD11, β-catenin and YAP, further revealing the link between the Wnt and Hippo pathways.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; KCTD11; Wnt pathway; YAP; β-catenin.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of zinc finger MIZ-type containing 2 as an oncoprotein enhancing NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 deacetylase activity to regulate Wnt and Hippo pathways in non-small-cell lung cancer.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Sep 12;29(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00636-z. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39266996 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte elevated gene-1(AEG-1) induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer through activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling.BMC Cancer. 2015 Mar 8;15:107. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1124-1. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25880337 Free PMC article.
-
SOX9 drives the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small-cell lung cancer through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.J Transl Med. 2019 May 6;17(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1895-2. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31060551 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between the Hippo Pathway and the Wnt Pathway in Huntington's Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders.Cells. 2022 Nov 16;11(22):3631. doi: 10.3390/cells11223631. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36429058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in lung cancer progression and therapy: a comprehensive review.Med Oncol. 2025 Apr 28;42(6):183. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02709-1. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40289194 Review.
Cited by
-
NF-κB in the Radiation Response of A549 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to X-rays and Carbon Ions under Hypoxia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 19;25(8):4495. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084495. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38674080 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal asthma and newborn DNA methylation.Clin Epigenetics. 2025 May 10;17(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13148-025-01858-4. Clin Epigenetics. 2025. PMID: 40349045 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the development and therapeutic resistance of non-small cell lung cancer.J Transl Med. 2024 Jun 13;22(1):565. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05380-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38872189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcuminoids as Modulators of EMT in Invasive Cancers: A Review of Molecular Targets With the Contribution of Malignant Mesothelioma Studies.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 8;13:934534. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.934534. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35873564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC02159 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression via ALYREF/YAP1 signaling.Mol Cancer. 2023 Aug 4;22(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01814-x. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37537569 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

