Comprehensive expressional analysis of chemosensitivity-related markers in large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung
- PMID: 34453496
- PMCID: PMC8520808
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.14102
Comprehensive expressional analysis of chemosensitivity-related markers in large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung
Abstract
Objectives: Various drug-sensitivity markers have been reported to be associated with tumor progression and chemotherapy resistance. Detailed expression profiles of sensitivity markers for cytotoxic chemotherapy in pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) remain unclear. Herein, we aimed to clarify the correlation between the expression of drug-sensitivity markers and clinicopathological features, prognostic impact, and status of tumor immunity in patients with LCNEC.
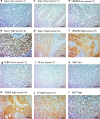
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the correlation between clinicopathological features and the expression of drug-sensitivity-related markers, including vascular endothelial growth factor 2 (VEGFR2), thymidylate synthase (TS), tubulin beta 3 class III (TUBB3), topoisomerase I (Topo-I), and Topo-II in 92 surgically resected LCNEC samples. Furthermore, we examined the prognostic significance of expression of these and their correlation with the immune cell status.
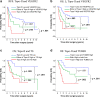
Results: Overall, high expression of TS, TUBB3, VEGFR2, Topo-I, and Topo-II was detected in 50 (54%), 31 (34%), 23 (25%), 65 (71%), and 36 (39%) samples, respectively. Univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that advanced pathological T and N factors, positive lymphatic permeation, and Topo-II expression were independent unfavorable prognosticators for recurrence-free survival, and advanced pathological T and N factors, Topo-II positive expression, and TS positive expression were independent unfavorable prognosticators for overall survival. In terms of correlation with immune cell status, higher expression of VEGFR2 was closely linked to negative PD-L1 expression.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that elevated Topo-II and TS expression may contribute to poor outcomes through protumoral biology in patients with LCNEC, and elevated VEGFR2 expression might negatively impact tumor immune reactions in LCNEC.
Keywords: chemosensitivity; large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma; lung cancer; thymidylate synthase; topoisomerase II.
© 2021 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors participated in this study and agreed with the content of this paper. K.K. has received research grants and honoraria for lectures from Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Bristol‐Myers Squibb. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical Significance of Various Drug-Sensitivity Markers in Patients with Surgically Resected Pulmonary Pleomorphic Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 24;11(11):1636. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111636. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31653009 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Biomarkers for Personalized Treatment in Pulmonary Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: A Comparative Analysis With Adenocarcinoma.Ann Thorac Surg. 2016 Nov;102(5):1694-1701. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.04.100. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016. PMID: 27368130
-
Analysis of 5-fluorouracil-related enzymes in pulmonary neuroendocrine carcinoma: differences in biological properties compared to epithelial carcinoma.Clin Lung Cancer. 2010 Nov 1;11(6):412-22. doi: 10.3816/CLC.2010.n.053. Clin Lung Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21062732
-
Treatment of lung large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):7047-57. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5003-4. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26943800 Review.
-
Treatment options for patients with large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung.Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014 Jun;62(6):351-6. doi: 10.1007/s11748-014-0379-9. Epub 2014 Apr 10. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014. PMID: 24719260 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Immunity-Related Gene Model Predicts Prognosis in Cholangiocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 1;12:791867. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.791867. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847907 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of VEGFR2 expression as a predictive marker of PD‑1 blockade in patients with advanced NSCLC.Oncol Rep. 2022 Dec;48(6):214. doi: 10.3892/or.2022.8429. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36281948 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 expression and immunotherapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Sci. 2022 Sep;113(9):3148-3160. doi: 10.1111/cas.15464. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Cancer Sci. 2022. PMID: 35722982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Committee for Scientific Affairs TJAfTS , Shimizu H, Okada M, Tangoku A, Doki Y, Endo S, et al. Thoracic and cardiovascular surgeries in Japan during 2017: annual report by the Japanese Association for Thoracic Surgery. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020;68:414–49. - PubMed
-
- Sherman S, Rotem O, Shochat T, Zer A, Moore A, Dudnik E. Efficacy of immune check‐point inhibitors (ICPi) in large cell neuroendocrine tumors of lung (LCNEC). Lung Cancer. 2020;143:40–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

