Apolipoprotein E regulates lipid metabolism and α-synuclein pathology in human iPSC-derived cerebral organoids
- PMID: 34453582
- PMCID: PMC8500881
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-021-02361-9
Apolipoprotein E regulates lipid metabolism and α-synuclein pathology in human iPSC-derived cerebral organoids
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Apolipoprotein E regulates lipid metabolism and α‑synuclein pathology in human iPSC‑derived cerebral organoids.Acta Neuropathol. 2022 Jan;143(1):119-121. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02380-6. Acta Neuropathol. 2022. PMID: 34724591 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
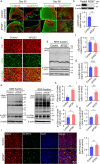
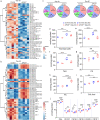
APOE4 is a strong genetic risk factor for Alzheimer's disease and Dementia with Lewy bodies; however, how its expression impacts pathogenic pathways in a human-relevant system is not clear. Here using human iPSC-derived cerebral organoid models, we find that APOE deletion increases α-synuclein (αSyn) accumulation accompanied with synaptic loss, reduction of GBA levels, lipid droplet accumulation and dysregulation of intracellular organelles. These phenotypes are partially rescued by exogenous apoE2 and apoE3, but not apoE4. Lipidomics analysis detects the increased fatty acid utilization and cholesterol ester accumulation in apoE-deficient cerebral organoids. Furthermore, APOE4 cerebral organoids have increased αSyn accumulation compared to those with APOE3. Carrying APOE4 also increases apoE association with Lewy bodies in postmortem brains from patients with Lewy body disease. Our findings reveal the predominant role of apoE in lipid metabolism and αSyn pathology in iPSC-derived cerebral organoids, providing mechanistic insights into how APOE4 drives the risk for synucleinopathies.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
G.B. consults for SciNeuro and E-Scape, and had consulted for AbbVie and Eisai. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Alzheimer's Association 2020 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2020 doi: 10.1002/alz.12068. - DOI
-
- Bassil F, Brown HJ, Pattabhiraman S, Iwasyk JE, Maghames CM, Meymand ES, et al. Amyloid-beta (Abeta) plaques promote seeding and spreading of alpha-synuclein and Tau in a mouse model of lewy body disorders with Abeta pathology. Neuron. 2020;105(260–275):e266. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.10.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RF1 AG068034/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG071226/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS074969/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013319/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG051504/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061796/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG027924/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG069701/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057181/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS110435/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046139/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062677/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG046205/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

