A review of physical and engineering factors potentially affecting shear wave elastography
- PMID: 34453649
- PMCID: PMC8578095
- DOI: 10.1007/s10396-021-01127-w
A review of physical and engineering factors potentially affecting shear wave elastography
Erratum in
-
Correction to: A review of physical and engineering factors potentially affecting shear wave elastography.J Med Ultrason (2001). 2021 Oct;48(4):415. doi: 10.1007/s10396-021-01159-2. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2021. PMID: 34669074 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
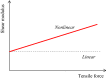
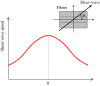
It has been recognized that tissue stiffness provides useful diagnostic information, as with palpation as a screening for diseases such as cancer. In recent years, shear wave elastography (SWE), a technique for evaluating and imaging tissue elasticity quantitatively and objectively in diagnostic imaging, has been put into practical use, and the amount of clinical knowledge about SWE has increased. In addition, some guidelines and review papers regarding technology and clinical applications have been published, and the status as a diagnostic technology is in the process of being established. However, there are still unclear points about the interpretation of shear wave speed (SWS) and converted elastic modulus in SWE. To clarify these, it is important to investigate the factors that affect the SWS and elastic modulus. Therefore, physical and engineering factors that potentially affect the SWS and elastic modulus are discussed in this review paper, based on the principles of SWE and a literature review. The physical factors include the propagation properties of shear waves, mechanical properties (viscoelasticity, nonlinearity, and anisotropy), and size and shape of target tissues. The engineering factors include the region of interest depth and signal processing. The aim of this review paper is not to provide an answer to the interpretation of SWS. It is to provide information for readers to formulate and verify the hypothesis for the interpretation. Therefore, methods to verify the hypothesis for the interpretation are also reviewed. Finally, studies on the safety of SWE are discussed.
Keywords: Engineering factors; Interpretation; Physical factors; Shear wave elastography; Shear wave speed.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There are no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography for Liver Disease. A Critical Appraisal of the Many Actors on the Stage.Ultraschall Med. 2016 Feb;37(1):1-5. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1567037. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Ultraschall Med. 2016. PMID: 26871407
-
Measurement of shear wave speed dispersion in the placenta by transient elastography: A preliminary ex vivo study.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 5;13(4):e0194309. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194309. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29621270 Free PMC article.
-
Two-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography of Normal Soft Tissue Organs in Adult Beagle Dogs; Interobserver Agreement and Sources of Variability.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Aug 19;8:979. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00979. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32974311 Free PMC article.
-
[New Diagnostic Imaging Technique - Shear Wave Elastography].Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2016 Fall;72(4):103-110. Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2016. PMID: 27860475 Review. Czech.
-
Assessing cardiac stiffness using ultrasound shear wave elastography.Phys Med Biol. 2022 Jan 17;67(2). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ac404d. Phys Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 34874312 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Assessment of Breast-Tumor Stiffness Using Shear-Wave Elastography Histograms.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Dec 13;12(12):3140. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12123140. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553148 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of the phase velocity dispersion curves for viscoelastic materials using Point Limited Shear Wave Elastography.Ultrasonics. 2025 Apr;148:107566. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2025.107566. Epub 2025 Jan 11. Ultrasonics. 2025. PMID: 39817930
-
Mechanical rheological model on the assessment of elasticity and viscosity in tissue inflammation: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 15;19(7):e0307113. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307113. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39008477 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Assessment of Shear Wave Propagation in Pennate Muscles Using an Automatic Ultrasound Probe Alignment System.IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol. 2023 Nov 30;4:259-267. doi: 10.1109/OJEMB.2023.3338090. eCollection 2023. IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 38196975 Free PMC article.
-
Quality Assurance of Point and 2D Shear Wave Elastography through the Establishment of Baseline Data Using Phantoms.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 31;24(15):4961. doi: 10.3390/s24154961. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39124008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shiina T, Nightingale KR, Palmeri ML, et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: part 1: basic principles and terminology. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41:1126–1147. - PubMed
-
- Barr RG, Nakashima K, Amy D, et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: part 2: breast. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41:1148–1160. - PubMed
-
- Ferraioli G, Filice C, Castera L, et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: part 3: liver. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41:1161–1179. - PubMed
-
- Kudo M, Shiina T, Moriyasu F, et al. JSUM ultrasound elastography practice guidelines: liver. J Med Ultrason. 2013;40:325–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

