Elabela prevents angiotensin II-induced apoptosis and inflammation in rat aortic adventitial fibroblasts via the activation of FGF21-ACE2 signaling
- PMID: 34453661
- PMCID: PMC8401356
- DOI: 10.1007/s10735-021-10011-3
Elabela prevents angiotensin II-induced apoptosis and inflammation in rat aortic adventitial fibroblasts via the activation of FGF21-ACE2 signaling
Abstract
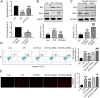
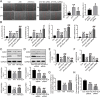
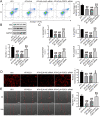
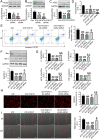
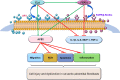
Apoptosis, inflammation, and fibrosis contribute to vascular remodeling and injury. Elabela (ELA) serves as a crucial regulator to maintain vascular function and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of hypertensive vascular remodeling. This study aims to explore regulatory roles and underlying mechanisms of ELA in rat aortic adventitial fibroblasts (AFs) in response to angiotensin II (ATII). In cultured AFs, exposure to ATII resulted in marked decreases in mRNA and protein levels of ELA, fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as well as increases in apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, and cellular migration, which were partially blocked by the exogenous replenishment of ELA and recombinant FGF21, respectively. Moreover, treatment with ELA strikingly reversed ATII-mediated the loss of FGF21 and ACE2 levels in rat aortic AFs. FGF21 knockdown with small interfering RNA (siRNA) significantly counterbalanced protective effects of ELA on ATII-mediated the promotion of cell migration, apoptosis, inflammatory, and oxidative injury in rat aortic AFs. More importantly, pretreatment with recombinant FGF21 strikingly inhibited ATII-mediated the loss of ACE2 and the augmentation of cell apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammatory injury in rat aortic AFs, which were partially prevented by the knockdown of ACE2 with siRNA. In summary, ELA exerts its anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-oxidant effects in rat aortic AFs via activation of the FGF21-ACE2 signaling. ELA may represent a potential candidate to predict vascular damage and targeting the FGF21-ACE2 signaling may be a promising therapeutic intervention for vascular adventitial remodeling and related disorders.
Keywords: Adventitial fibroblasts; Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; Apoptosis; Elabela; Fibroblast growth factor 21; Inflammation.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elabela blunts doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress and ferroptosis in rat aortic adventitial fibroblasts by activating the KLF15/GPX4 signaling.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 Jan;28(1):91-103. doi: 10.1007/s12192-022-01317-6. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023. PMID: 36510036 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-122 aggravates angiotensin II-mediated apoptosis and autophagy imbalance in rat aortic adventitial fibroblasts via the modulation of SIRT6-elabela-ACE2 signaling.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 15;883:173374. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173374. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32682786 Free PMC article.
-
Transactivation domain of Krüppel-like factor 15 negatively regulates angiotensin II-induced adventitial inflammation and fibrosis.FASEB J. 2019 May;33(5):6254-6268. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801809R. Epub 2019 Feb 18. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30776250
-
Insights into the role of FGF21 in coronary heart disease.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Dec;282(Pt 5):136911. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136911. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39476920 Review.
-
Functions of FGF21 and its role in cardiac hypertrophy.J Adv Res. 2025 Mar 13:S2090-1232(25)00148-1. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2025.03.007. Online ahead of print. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 40089060 Review.
Cited by
-
Elabela blunts doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress and ferroptosis in rat aortic adventitial fibroblasts by activating the KLF15/GPX4 signaling.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 Jan;28(1):91-103. doi: 10.1007/s12192-022-01317-6. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023. PMID: 36510036 Free PMC article.
-
ACE2 in chronic disease and COVID-19: gene regulation and post-translational modification.J Biomed Sci. 2023 Aug 22;30(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12929-023-00965-9. J Biomed Sci. 2023. PMID: 37608279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sexual Dimorphism in the Polarization of Cardiac ILCs through Elabela.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Dec 30;45(1):223-232. doi: 10.3390/cimb45010017. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36661503 Free PMC article.
-
ACE2/ACE imbalance mediates bisphenol A-induced lung injury in Wistar rats: Results from captopril versus losartan histo-biochemical study.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 4;9(11):e22056. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22056. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027817 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Suppressed Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induced by Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase.Cardiol Res. 2024 Oct;15(5):404-414. doi: 10.14740/cr1705. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Cardiol Res. 2024. PMID: 39420979 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

