A novel angular dependency model for MatriXX response and its application to true composite dose verification for IMRT plans
- PMID: 34453876
- PMCID: PMC8504602
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13405
A novel angular dependency model for MatriXX response and its application to true composite dose verification for IMRT plans
Abstract
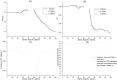
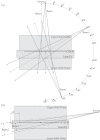
Purpose: This paper proposes a model for the angular dependency of MatriXX response and investigates whether MatriXX, with the angular-model-based approach can be applied to true composite dose verification for IMRT plans.
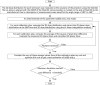
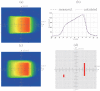
Method: This model attributes the angular dependence of MatriXX response to dynamical translation of its effective measurement plane (EMP) due to the change of beam angle. Considering this mechanism, true composite dose verifications for IMRT plans specified in AAPM TG 119 report using both MatriXX and Gafchromic EBT3 films were undertook and compared to validate the applicability of MatriXX for patient specific QA of composite beam IMRT plans. Dose verifications using MatriXX with and without angular-model-based approach were performed.
Results: MatriXX with angular-model-based approach achieved gamma passing rates with 3%/3 mm and 3%/2 mm criteria better than 98.3% and 98.1% respectively for true composite dose verification of plans in AAPM TG 119 report. The 3%/3 mm and 3%/2 mm gamma passing rates using MatriXX without angular-model-based approach ranged from 85.8% to 98.2% and from 81.3% to 96.5%, respectively. The p-values from the single sided paired t-test indicated no statistical difference between the passing rates from MatriXX with angular-model-based approach and from films, and significant difference between the passing rates from uncorrected MatriXX and from films.
Conclusion: The proposed model for angular dependent MatriXX response is necessary and effective. Dose verification using MatriXX with angular-model-based approach is acceptable for true composite beam IMRT plans with required accuracy to simplify patient specific QA.
Keywords: IMRT; MatriXX; angular response; mechanism of angular dependency; patient specific QA; radiotherapy; true composite dose verification.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of The American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Figures



References
-
- IBA Dosimetry (DE) . myQA user's guide vol.1, myQA platform and devices. Schwarzenbruck (DE): IBA; 2017.
-
- Amerio S, Boriano A, Bourhaleb F, et al. Dosimetric characterization of a large area pixel‐segmented ionization chamber. Med Phys. 2004;31(2):414–420. - PubMed
-
- Bortfeld T. IMRT: a review and preview. Phys Med Biol. 2006;51(13):R363‐79. - PubMed
-
- Herzen J, Todorovic M, Cremers F, et al. Dosimetric evaluation of a 2D pixel ionization chamber for implementation in clinical routine. Phys Med Biol. 2007;52(4):1197–1208. - PubMed
-
- Han Z, Ng SK, Bhagwat MS, Lyatskaya Y, Piotr Zygmanski P. Evaluation of MatriXX for IMRT and VMAT dose verifications in peripheral dose regions. Med Phys. 2010;37(7):3704–3714. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

