Conformational equilibria in allosteric control of Hsp70 chaperones
- PMID: 34453889
- PMCID: PMC8500941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.07.039
Conformational equilibria in allosteric control of Hsp70 chaperones
Abstract
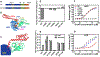
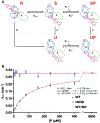
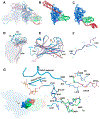
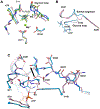
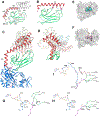
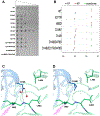
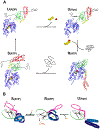
Heat-shock proteins of 70 kDa (Hsp70s) are vital for all life and are notably important in protein folding. Hsp70s use ATP binding and hydrolysis at a nucleotide-binding domain (NBD) to control the binding and release of client polypeptides at a substrate-binding domain (SBD); however, the mechanistic basis for this allostery has been elusive. Here, we first characterize biochemical properties of selected domain-interface mutants in bacterial Hsp70 DnaK. We then develop a theoretical model for allosteric equilibria among Hsp70 conformational states to explain the observations: a restraining state, Hsp70R-ATP, restricts ATP hydrolysis and binds peptides poorly, whereas a stimulating state, Hsp70S-ATP, hydrolyzes ATP rapidly and has high intrinsic substrate affinity but rapid binding kinetics. We support this model for allosteric regulation with DnaK structures obtained in the postulated stimulating state S with biochemical tests of the S-state interface and with improved peptide-binding-site definition in an R-state structure.
Keywords: DnaK; Hsp70; allosteric regulation; crystal structure; molecular chaperone; protein folding.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung L-W, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, and Zwart PH (2010). PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D 66, 213–221. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anfinsen CB (1973). Principles that govern the folding of protein chains. Science 181, 223–230. - PubMed
-
- Buchberger A, Theyssen H, Schroder H, McCarty JS, Virgallita G, Milkereit P, Reinstein J, and Bukau B (1995). Nucleotide-induced conformational changes in the ATPase and substrate binding domains of the DnaK chaperone provide evidence for interdomain communication. J. Biol. Chem 270, 16903–16910. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

