Microbiome therapeutics for hepatic encephalopathy
- PMID: 34453966
- PMCID: PMC10471317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.08.004
Microbiome therapeutics for hepatic encephalopathy
Abstract
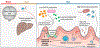
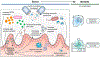
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a complication of cirrhosis characterised by neuropsychiatric and motor dysfunction. Microbiota-host interactions play an important role in HE pathogenesis. Therapies targeting microbial community composition and function have been explored for the treatment of HE. Prebiotics, probiotics and faecal microbiota transplant (FMT) have been used with the aim of increasing the abundance of potentially beneficial taxa, while antibiotics have been used to decrease the abundance of potentially harmful taxa. Other microbiome therapeutics, including postbiotics and absorbents, have been used to target microbial products. Microbiome-targeted therapies for HE have had some success, notably lactulose and rifaximin, with probiotics and FMT also showing promise. However, there remain several challenges to the effective application of microbiome therapeutics in HE, including the resilience of the microbiome to sustainable change and unpredictable clinical outcomes from microbiota alterations. Future work in this space should focus on rigorous trial design, microbiome therapy selection, and a personalised approach to HE.
Keywords: ammonia; cirrhosis; fecal transplant; lactulose; probiotic; rifaximin.
Copyright © 2021 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest Patricia P. Bloom serves as a consultant for Synlogic. ASL: no conflict. VBY serves as a consultant to Vedanta, Bio-K+ International and Pantheryx. Elliot Tapper has served as consultant for Axcella, Kaleido, Mallinckrodt, Novo Nordisk, Allergan, and Takeida. He has received unrestricted grants from Valeant and Gilead. Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further details.
Figures

References
-
- Bajaj JS, O’Leary JG, Tandon P, Wong F, Garcia-Tsao G, Kamath PS, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy is associated with mortality in patients with cirrhosis independent of other extrahepatic organ failures. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;15(4):565–574.e4. - PubMed
-
- Rabiee A, Ximenes RO, Nikayin S, Hickner A, Juthani P, Rosen RH, et al. Factors associated with health-related quality of life in patients with cirrhosis: a systematic review. Liver Int 2020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

