Heparin-binding protein is significantly increased in acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 34454419
- PMCID: PMC8403433
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-021-01910-6
Heparin-binding protein is significantly increased in acute pancreatitis
Abstract
Background: Most patients with acute pancreatitis (AP) experience mild, self-limiting disease with little or no need for hospital care. However, 20-25% of patients develop a more severe and potentially life-threatening condition with progressive systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and multiorgan failure, resulting in high morbidity and mortality rates. Predicting disease severity at an early stage is important, as immediate supportive care has been demonstrated to reduce the incidence of SIRS and organ failure, improving patient outcome. Several studies have demonstrated elevated levels of heparin-binding protein (HBP) in patients with sepsis and septic shock, and HBP is believed to play a part in endothelial dysfunction leading to vascular leakage. As HBP levels increase prior to other known biomarkers, HBP has emerged as a promising early predictor of severe sepsis with organ dysfunction.
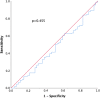
Methods: Patients admitted to Skåne University Hospital in Malmö between 2010 and 2013 fulfilling the criteria for AP were identified in the emergency department and prospectively enrolled in this study. The primary outcome was measured levels of HBP upon hospital admission in patients with confirmed AP. Correlations among HBP concentrations, disease severity and fluid balance were considered secondary endpoints. The correlation between HBP levels and fluid balance were analysed using Pearson correlation, and the ability of HBP to predict moderately severe/severe AP was assessed using a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
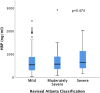
Results: The overall median HBP level in this study was 529 (307-898) ng/ml. There were no significant group differences in HBP levels based on AP severity. Fluid balance differed significantly between patients with mild versus moderately severe and severe pancreatitis, but we found no correlation between HBP concentration and fluid balance.
Conclusions: HBP levels are dramatically increased in patients with AP, and these levels far exceed those previously reported in other conditions. In this study, we did not observe any significant correlation between HBP levels and disease severity or the need for intravenous fluid. Additional studies on HBP are needed to further explore the role of HBP in the pathogenesis of AP and its possible clinical implications.
Keywords: Acute pancreatitis; Biomarkers; Heparin-binding protein.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- de-Madaria E, Martinez J, Perez-Mateo M. The dynamic nature of fluid resuscitation in acute pancreatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10(1):95–6; author reply 96. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous