The landscape of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in advanced lung cancer
- PMID: 34454455
- PMCID: PMC8403352
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08662-2
The landscape of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in advanced lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The advent of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) therapy has resulted in significant survival benefits in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) without increasing toxicity. However, the utilisation of immunotherapy for small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) remains unclear, with a scarcity of systematic comparisons of therapeutic effects and safety of immunotherapy in these two major lung cancer subtypes. Herein, we aimed to provide a comprehensive landscape of immunotherapy and systematically review its specific efficacy and safety in advanced lung cancer, accounting for histological types.
Methods: We identified studies assessing immunotherapy for lung cancer with predefined endpoints, including overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), and treatment-related adverse events (TRAE), from PubMed, Embase, Medline, and Cochrane library. A random-effects or fixed-effect model was adopted according to different settings.
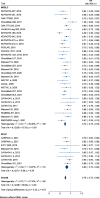
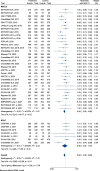
Results: Overall, 38 trials with 20,173 patients with lung cancer were included in this study. ICI therapy resulted in a significantly prolonged survival in both patients with NSCLC and SCLC when compared with chemotherapy (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.74; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.70-0.79] and [HR = 0.82; 95% CI, 0.75-0.90], respectively). The magnitude of disease control and survival benefits appeared superior with ICI plus standard of care (SOC) when compared with SOC alone. OS and PFS advantages were observed only when immunotherapy was employed as the first-line treatment in patients with SCLC.
Conclusion: ICI therapy is a promising therapeutic option in patients with NSCLC and SCLC. ICI plus SOC can be recommended as the optimal first-line treatment for patients with SCLC, and double-target ICIs combined with SOC are recommended in patients with NSCLC as both the first and subsequent lines of treatment. Additionally, non-first-line immunotherapy is not recommended in patients with SCLC.
Keywords: Efficacy; Immune checkpoint inhibitor; Non-small-cell lung cancer; Small-cell lung cancer.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared that there was no conflict of interests.
Figures




References
-
- Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V, Harewood R, Matz M, Niksic M, Bonaventure A, Valkov M, Johnson CJ, Esteve J, et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000–14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet (London, England) 2018;391(10125):1023–1075. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33326-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard D, Cho BC, Gray JE, Ohe Y, Zhou C, Reungwetwattana T, Cheng Y, Chewaskulyong B, Shah R, Cobo M, Lee KH, Cheema P, Tiseo M, John T, Lin MC, Imamura F, Kurata T, Todd A, Hodge R, Saggese M, Rukazenkov Y, Soria JC. Overall survival with Osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(1):41–50. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1913662. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

