Low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels are associated with malignant intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: A multicenter study
- PMID: 34454509
- PMCID: PMC8399724
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-021-01523-8
Low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels are associated with malignant intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: A multicenter study
Abstract
Background: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) can potentially undergo malignant transformation. Studies have shown that high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) was associated with the risk of cancer. In this study, the association between HDL-c and the incidence of malignancy in IPMNs was investigated.
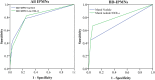
Materials and methods: 226 patients with histologically proven IPMNs who underwent surgery were included in the present study. Patients were assigned to a training group (n = 151) and validation group (n = 75). Patients' demographic information, clinical data, and histopathological evaluation findings were obtained from medical records. Malignant IPMNs were defined as lesions that showed high grade dysplasia and invasive carcinoma. Logistic regression analyses were used to show the association between HDL-c and malignant IPMNs. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated to analyze predictive performance.
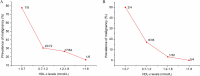
Results: The prevalence of low HDL-c levels was higher in patients with malignant IPMNs than in those with non-malignant IPMNs (P < 0.01) in both the training group and validation group. The prevalence of malignant IPMNs decreased with an increase in HDL-c levels both in patients with all types of IPMNs, as well as in those with branch-duct IPMNs (BD-IPMNs).Logistic analysis showed that low HDL-c levels were associated with malignant IPMNs (odds ratio (OR) = 20.56, 95 % confidence interval (CI): 2.58-163.64, P < 0.01) in all types of IPMNs and BD-IPMNs (OR = 17.6, 95 %CI: 1.16-268.46, P = 0.02 ).The predictive performance of mural nodules plus low HDL-c levels was higher than that of mural nodules alone or mural nodules plus cyst size for the identification of malignant BD-IPMNs.
Conclusions: HDL-c levels may serve a potential biomarker for identifying malignant IPMNs and improve the predictive ability of malignancy in BD-IPMNs.
Keywords: HDL-cholesterol; branch duct; intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms; invasive carcinoma; lipids; malignancy; pancreas.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors of malignancy in pure branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: A nationwide multicenter study.Pancreatology. 2015 Jul-Aug;15(4):405-10. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2015.04.010. Epub 2015 May 7. Pancreatology. 2015. PMID: 25998516
-
Predictors of Malignancy in "Pure" Branch-Duct Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of the Pancreas without Enhancing Mural Nodules on CT Imaging: A Nationwide Multicenter Study.Gut Liver. 2018 Sep 15;12(5):583-590. doi: 10.5009/gnl17582. Gut Liver. 2018. PMID: 29730906 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Multi-institutional Preoperative Nomogram for Predicting Grade of Dysplasia in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms (IPMNs) of the Pancreas: A Report from The Pancreatic Surgery Consortium.Ann Surg. 2018 Jan;267(1):157-163. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002015. Ann Surg. 2018. PMID: 28079542 Free PMC article.
-
Cyst features and risk of malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a meta-analysis.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Aug;11(8):913-21; quiz e59-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.02.010. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23416279 Review.
-
Treatment of branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: state of the art.Updates Surg. 2016 Sep;68(3):265-271. doi: 10.1007/s13304-016-0386-8. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Updates Surg. 2016. PMID: 27502606 Review.
Cited by
-
The association between serum lipid levels and histological type of breast cancer.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Aug 19;27(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00784-y. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35986413 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical relevance of serum lipids in the carcinogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Apr 3;23(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-02859-6. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37013557 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of the monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio in the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients after surgery.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 Apr 30;14(4):1340-1350. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-2025-171. Epub 2025 Apr 27. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40386725 Free PMC article.
-
The associations between serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and malignant behavior in pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms.Lipids Health Dis. 2022 Jul 16;21(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01669-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 35842659 Free PMC article.
-
The association between serum ferritin levels and malignant intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.BMC Cancer. 2021 Nov 20;21(1):1253. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08986-z. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34800987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hruban RH, Takaori K, Klimstra DS, Adsay NV, Albores-Saavedra J, Biankin AV, et al. An illustrated consensus on the classification of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28(8):977–87. doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000126675.59108.80. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fritz S, Hackert T, Hinz U, Hartwig W, Büchler MW, Werner J. Role of serum carbohydrate antigen 19 – 9 and carcinoembryonic antigen in distinguishing between benign and invasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Br J Surg. 2011;98(1):104–10. doi: 10.1002/bjs.7280. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

